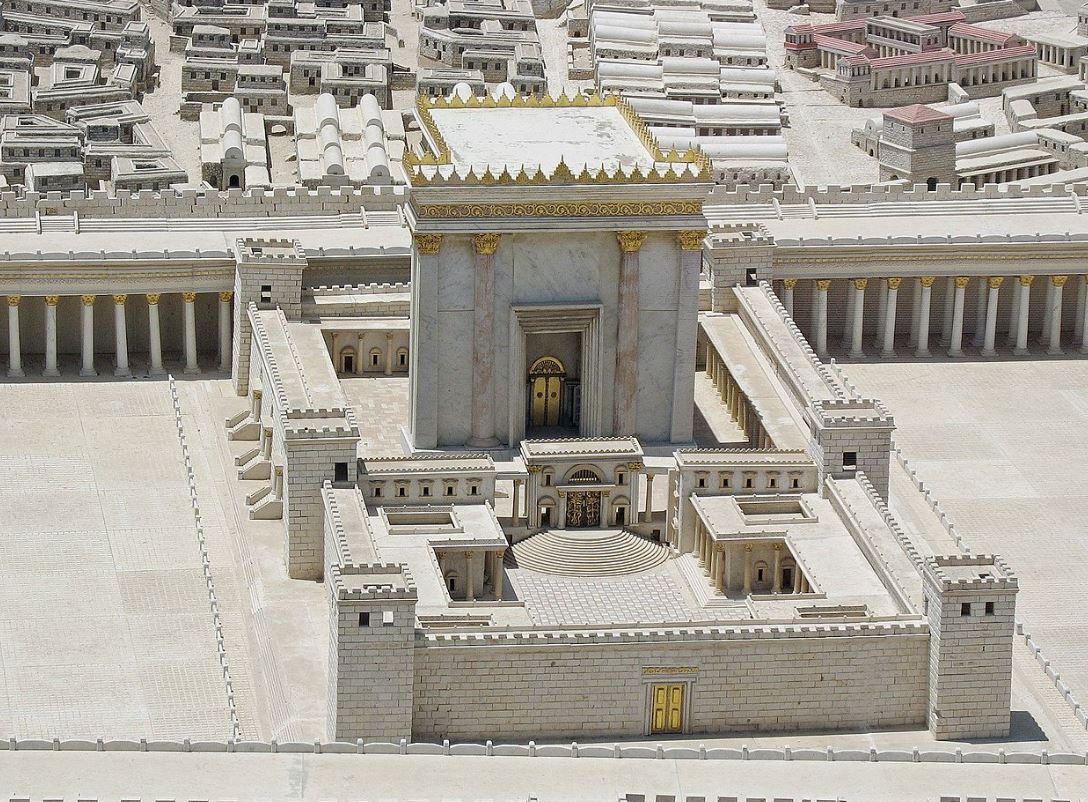
After concluding that mechitza means a wall, the Gemara now brings an alternate version of the previous sugya in which the opposite conclusion is reached – that mechitza is a partition, concluding that one is responsible for preventing heizek re’iya, one neighbor looking into the other’s courtyard. Two difficulties are raised against this explanation but are resolved. To resolve the second difficulty, Rabbi Asi brings Rabbi Yochanan’s understanding of the Mishna that the case is a courtyard that is less than 4×4 cubits and too small to require dividing. Several difficulties are brought on that understanding and are resolved. The Gemara clarifies the differences between the bricks and stones mentioned in the Mishna. The Gemara infers from the Mishna’s line that a wall four cubits high is built from gazit which is five handbreadths wide, then if it is eight cubits in height, the wall needs to be ten handbreadths wide to be sturdy. If so, in the first Temple, how did the wall of the ama taraksin (separating the kodesh from the kodesh kodashim), made of gazit, stand if it was thirty cubits in height and six handbreadths wide? Why did they use a parochet, not a wall, in the second Temple? Rav Chisda rules that one cannot knock down a shul unless one already has a new shul in its place. This leads to a story about Herod and the rebuilding of the Temple and his rise to power.
Bava Batra
Masechet Bava Batra is sponsored by Lori Stark in loving memory of her mother in law, Sara Shapiro z”l and her father Nehemiah Sosewitz z”l.
This month’s learning is dedicated to the refuah shleima of our dear friend, Phyllis Hecht, גיטל פעשא בת מאשה רחל by all her many friends who love and admire her. Phyllis’ emuna, strength, and positivity are an inspiration.
This week’s learning is sponsored by Nira Feldman in loving memory of her mother, Faye Darack Z’L 3rd yahrzeit. “She was a dedicated Hadran learner and continues to inspire us with her curiosity and love of learning each day. We miss her deeply.”
This week’s learning is sponsored by Nira Feldman in loving memory of her mother, Faye Darack Z’L 3rd yahrzeit. “She was a dedicated Hadran learner and continues to inspire us with her curiosity and love of learning each day. We miss her deeply.”
Want to dedicate learning? Get started here:

Today’s daily daf tools:
Bava Batra
Masechet Bava Batra is sponsored by Lori Stark in loving memory of her mother in law, Sara Shapiro z”l and her father Nehemiah Sosewitz z”l.
This month’s learning is dedicated to the refuah shleima of our dear friend, Phyllis Hecht, גיטל פעשא בת מאשה רחל by all her many friends who love and admire her. Phyllis’ emuna, strength, and positivity are an inspiration.
This week’s learning is sponsored by Nira Feldman in loving memory of her mother, Faye Darack Z’L 3rd yahrzeit. “She was a dedicated Hadran learner and continues to inspire us with her curiosity and love of learning each day. We miss her deeply.”
This week’s learning is sponsored by Nira Feldman in loving memory of her mother, Faye Darack Z’L 3rd yahrzeit. “She was a dedicated Hadran learner and continues to inspire us with her curiosity and love of learning each day. We miss her deeply.”
Today’s daily daf tools:
Delve Deeper
Broaden your understanding of the topics on this daf with classes and podcasts from top women Talmud scholars.
New to Talmud?
Check out our resources designed to help you navigate a page of Talmud – and study at the pace, level and style that fits you.
The Hadran Women’s Tapestry
Meet the diverse women learning Gemara at Hadran and hear their stories.
Bava Batra 3
דְּאִיצְטַנַּע מִינָּךְ.
so that I can hide from you at that time and avoid coming under your gaze.
לִישָּׁנָא אַחֲרִינָא אָמְרִי לַהּ: סַבְרוּהָ, מַאי ״מְחִיצָה״ – פְּלוּגְתָּא, דִּכְתִיב: ״וַתְּהִי מֶחֱצַת הָעֵדָה״; וְכֵיוָן דְּרָצוּ – בּוֹנִין אֶת הַכּוֹתֶל בְּעַל כּוֹרְחָן, אַלְמָא הֶיזֵּק רְאִיָּה שְׁמֵיהּ הֶיזֵּק.
§ The Gemara has so far presented one version of the discussion of the mishna. A different version relates the discussion as follows: The Sages initially assumed: What is the meaning of the term meḥitza mentioned in the mishna? A division, not a partition, as it is written: “And the division of [meḥetzat] the congregation was” (Numbers 31:43). According to this interpretation, the mishna means to say: Since they wished to divide the jointly owned courtyard, they build a proper wall in the center even against the will of one of the partners. Apparently, it may be concluded that damage caused by sight is called damage.
אֵימָא: מַאי ״מְחִיצָה״ – גּוּדָּא; דִּתְנַן: מְחִיצַת הַכֶּרֶם שֶׁנִּפְרְצָה – אוֹמֵר לוֹ: ״גְּדוֹר״. נִפְרְצָה – אוֹמֵר לוֹ: ״גְּדוֹר״. נִתְיָאֵשׁ הֵימֶנָּה וְלֹא גְּדָרָהּ – הֲרֵי זֶה קִידֵּשׁ, וְחַיָּיב בְּאַחְרָיוּתָהּ.
The Gemara objects to this conclusion: But why not say: What is the meaning of the term meḥitza mentioned in the mishna? It means a partition. This usage would be as we learned in a baraita: Consider the case where a partition of [meḥitzat] a vineyard which separates the vineyard from a field of grain was breached, resulting, if the situation is not rectified, in the grain and grapes becoming items from which deriving benefit is prohibited. The owner of the field of grain may say to the owner of the vineyard: Build a partition between the vineyard and the field of grain. If the owner of the vineyard did so, and the partition was breached again, the owner of the field of grain may say to him again: Build a partition. If the owner of the vineyard neglected to make the necessary repairs and did not properly build a partition between the fields, the grain and grapes are rendered forbidden due to the prohibition of diverse kinds planted in a vineyard, and he is liable for the monetary loss.
וְטַעְמָא דְּרָצוּ, הָא לֹא רָצוּ – אֵין מְחַיְּיבִין אוֹתוֹ, אַלְמָא הֶיזֵּק רְאִיָּה לָאו שְׁמֵיהּ הֶיזֵּק!
The Gemara concludes stating the objection: And according to the understanding that the term meḥitza means a partition, one can infer: The reason that they build a wall is that they both wished to make a partition in their jointly owned courtyard. But if they did not both wish to do so, the court does not obligate the reluctant partner to build such a wall, although his neighbor objects to the fact that the partner can see what he is doing in his courtyard. Apparently, it may be concluded that damage caused by sight is not called damage.
אִי הָכִי, ״בּוֹנִין אֶת הַכּוֹתֶל״?! ״בּוֹנִין אוֹתוֹ״ מִבְּעֵי לֵיהּ! אֶלָּא מַאי – פְּלוּגְתָּא? אִי הָכִי, ״שֶׁרָצוּ לַעֲשׂוֹת מְחִיצָה״?! ״שֶׁרָצוּ לַחֲצוֹת״ מִבְּעֵי לֵיהּ! כִּדְאָמְרִי אִינָשֵׁי: תָּא נַעֲבֵיד פְּלוּגְתָּא.
The Gemara rejects this argument: If so, the words: They build the wall, are imprecise, as the tanna should have said: They build it, since the wall and the partition are one and the same. The Gemara retorts: Rather, what is the meaning of the term meḥitza? A division. If it is so that the term meḥitza means a division, the words: Who wished to make a division, are imprecise, as the tanna should have said: Who wished to divide. The Gemara answers: The phrasing of the mishna is as people commonly say: Come, let us make a division. Consequently, the mishna can also be understood as referring to two people who wished to divide a jointly owned area.
וְאִי הֶיזֵּק רְאִיָּה שְׁמֵיהּ הֶיזֵּק – מַאי אִירְיָא רָצוּ? אֲפִילּוּ לֹא רָצוּ נָמֵי! אָמַר רַבִּי אַסִּי אָמַר רַבִּי יוֹחָנָן: מִשְׁנָתֵנוּ – כְּשֶׁאֵין בָּהּ דִּין חֲלוּקָהּ, וְהוּא דְּרָצוּ.
The Gemara asks, according to the understanding that meḥitza means division: But if damage caused by sight is called damage, why does the tanna specifically teach that if they wish, they build a wall? Even if they did not both wish to do so, it should also be possible to compel the reluctant party to build a wall between them. Rabbi Asi said that Rabbi Yoḥanan said: Our mishna is referring to a courtyard that is not subject to the halakha of division. Joint owners of a courtyard cannot be compelled to divide the courtyard unless each party will receive at least four square cubits of the courtyard. And therefore, this ruling of the mishna applies only in the case where they both wished to divide the courtyard.
מַאי קָא מַשְׁמַע לַן – דְּכִי לֵית בֵּיהּ דִּין חֲלוּקָהּ, כִּי רָצוּ – פְּלִיגִי?! תְּנֵינָא: אֵימָתַי – בִּזְמַן שֶׁאֵין שְׁנֵיהֶם רוֹצִים, אֲבָל בִּזְמַן שֶׁשְּׁנֵיהֶם רוֹצִים – אֲפִילּוּ פָּחוֹת מִכָּאן חוֹלְקִין! אִי מֵהָתָם, הֲוָה אָמֵינָא אֲפִילּוּ פָּחוֹת מִכָּאן – בִּמְסִיפָס בְּעָלְמָא; קָא מַשְׁמַע לַן הָכָא, כּוֹתֶל.
The Gemara asks: According to this understanding, what is the tanna teaching us? Is he teaching us that when a courtyard is not subject to the halakha of division, if they nevertheless wished to do so, they divide it? But we already learned this in the latter clause of a different mishna (11a): When do they not divide the courtyard because it is not large enough to compel division? When the joint owners do not both wish to divide it. But when both of them wish to divide it, they divide it even if it is smaller than this, i.e., smaller than four square cubits for each party. The Gemara answers: If we had learned this halakha only from there, I would say that they divide the courtyard even if it is smaller than this by constructing a mere partition of pegs, which does not prevent invasion of privacy. Therefore, the tanna teaches us here in this mishna that if they wish to divide the courtyard they can be compelled to build a proper wall.
וְלִיתְנֵי הָא וְלָא לִיתְנֵי הָךְ! סֵיפָא אִיצְטְרִיכָא לֵיהּ – וְכִתְבֵי הַקֹּדֶשׁ, אַף עַל פִּי שֶׁשְּׁנֵיהֶם רוֹצִים – לֹא יַחְלוֹקוּ.
The Gemara asks: If so, let the tanna teach this mishna and not teach that other mishna, as this mishna teaches more details than the later one. The Gemara answers: It was necessary for the tanna to teach the other mishna to introduce the last clause of that mishna, which states: And jointly owned sacred writings that are contained in a single scroll should not be divided even if both owners wish to do so.
(לִישָּׁנָא אַחֲרִינָא: וְכִי רָצוּ מַאי הָוֵי? לִיהְדַּר בֵּיהּ! אָמַר רַב אַסִּי אָמַר רַבִּי יוֹחָנָן: בְּשֶׁקָּנוּ מִיָּדוֹ כּוּ׳.
The Gemara brings a different version of the previous discussion: And if they wished to divide the courtyard, what of it? What forces them to build the wall? If one of the parties does not wish to build a wall, let him retract. Rav Asi said that Rabbi Yoḥanan said that the mishna is not discussing a case where they merely reached a verbal agreement to divide the courtyard, but rather with a case where each party performed an act of acquisition with the other, confirming their respective commitments. Therefore, neither side can retract.
אַדְּאַשְׁמְעִינַן בְּשֶׁאֵין בָּהּ דִּין חֲלוּקָהּ – וְהוּא דְּרָצוּ, לַישְׁמְעִינַן בְּיֵשׁ בָּהּ דִּין חֲלוּקָהּ – וְאַף עַל גַּב דְּלֹא רָצוּ! אִי אַשְׁמְעִינַן בְּיֵשׁ בָּהּ דִּין חֲלוּקָהּ – וְאַף עַל גַּב דְּלֹא רָצוּ, הֲוָה אָמֵינָא: שֶׁאֵין בָּהּ דִּין חֲלוּקָהּ – אֲפִילּוּ רָצוּ נָמֵי לָא; קָא מַשְׁמַע לַן.
The Gemara asks: Rather than teaching us a case where the courtyard is not subject to the halakha of division, but nevertheless they wished to divide it, let the mishna teach us a case where the courtyard is subject to the halakha of division, even if they did not both wish to divide it. The Gemara answers: Had it taught us only a case where the courtyard is subject to the halakha of division that applies even if they did not both wish to divide it, I would say that in a case where the courtyard is not subject to the halakha of division then even if they both wished to divide it, if one of the parties does not wish to build a proper wall he cannot be compelled to do so. Therefore, the mishna teaches us that he is compelled to participate.
וּמִי מָצֵית אָמְרַתְּ הָכִי?! וְהָא קָתָנֵי סֵיפָא: אֵימָתַי – בִּזְמַן שֶׁאֵין שְׁנֵיהֶם רוֹצִים, אֲבָל בִּזְמַן שֶׁשְּׁנֵיהֶם רוֹצִים – יַחְלוֹקוּ. מַאי, לָאו אַכּוֹתֶל? לָא, אַמְּסִיפָס בְּעָלְמָא.
The Gemara asks: But how can you say this? Doesn’t the latter clause of the mishna (11a) teach: When do they not divide the courtyard because it is not large enough to compel division? When the joint owners do not both wish to divide it. But when both of them wish to divide it, they divide it even if it is smaller than this. What, is this clause of the mishna not referring to the fact that either one can force the other to build a proper wall? The Gemara answers: No, it is referring to a mere partition of pegs and not to an actual wall.
לִיתְנֵי הַאי וְלָא לִיתְנֵי הַאי! סֵיפָא אִצְטְרִיכָא לֵיהּ – וּבְכִתְבֵי הַקֹּדֶשׁ, אַף עַל פִּי שֶׁשְּׁנֵיהֶם רוֹצִים – לֹא יַחְלוֹקוּ).
The Gemara asks: If so, let the tanna teach this mishna and not teach that other mishna, as this mishna teaches more details than the later one. The Gemara answers: It was necessary to teach the other mishna for the last clause of that mishna, which states: And jointly owned sacred writings that are contained in a single scroll should not be divided even if both owners wish to do so. This concludes the alternative version of the discussion.
בְּמַאי אוֹקֵימְתָּא לְמַתְנִיתִין – בְּשֶׁאֵין בָּהּ דִּין חֲלוּקָהּ; אִי בְּשֶׁאֵין בָּהּ דִּין חֲלוּקָהּ, כִּי רָצוּ מַאי הָוֵי? נֶהְדְּרוּ בְּהוּ! אָמַר רַבִּי אַסִּי אָמַר רַבִּי יוֹחָנָן: שֶׁקָּנוּ מִיָּדָן.
The Gemara continues its analysis of the mishna: To what case did you interpret the mishna to be referring? To a case where the courtyard is not subject to the halakha of division. But if there is no halakha of division, then if they wished to divide the courtyard, what of it; how can either one force the other to build a wall? If the parties no longer want to build a wall, let them retract. Rabbi Asi said that Rabbi Yoḥanan said: It is referring to a case where each party performed an act of acquisition with the other, confirming their respective commitments. Therefore, neither party can retract.
וְכִי קָנוּ מִיָּדָן מַאי הָוֵי? קִנְיַן דְּבָרִים בְּעָלְמָא הוּא! בְּשֶׁקָּנוּ מִיָּדָן בְּרוּחוֹת. רַב אָשֵׁי אָמַר: כְּגוֹן שֶׁהָלַךְ זֶה בְּתוֹךְ שֶׁלּוֹ וְהֶחֱזִיק, וְזֶה בְּתוֹךְ שֶׁלּוֹ וְהֶחֱזִיק.
The Gemara asks: But even if each party performed an act of acquisition with the other, what of it? It is merely a verbal acquisition, meaning there was no actual transfer of property, but only a verbal agreement to act in a certain manner in the future and not a true act of acquisition. The Gemara answers: They performed an act of acquisition with the other with regard to directions, i.e., not only did they verbally agree to divide the courtyard, they also determined which of them would get which part of the courtyard. Consequently, the acquisition related to actual property, a particular plot of land. Rav Ashi said: For example, this one walked through his designated portion and performed an act demonstrating ownership there, and that one walked through his designated portion and performed an act demonstrating ownership there.
מָקוֹם שֶׁנָּהֲגוּ לִבְנוֹת כּוּ׳. גְּוִיל – אַבְנֵי דְּלָא מְשַׁפְּיָא. גָּזִית – אַבְנֵי דִּמְשַׁפְּיָא, דִּכְתִיב: ״כָּל אֵלֶּה אֲבָנִים יְקָרוֹת כְּמִדּוֹת גָּזִית (וְגוֹ׳)״ כְּפִיסִין – אַרְחֵי. לְבֵינִין – לִיבְנֵי.
§ The mishna teaches: In a place where it is customary to build such a wall with non-chiseled stone [gevil], or chiseled stone [gazit], or small bricks [kefisin], or large bricks [leveinim], they must build the wall with that material. The Gemara identifies the various building materials: Gevil refers to stones that are not planed. Gazit means stones that are planed, as it is written: “All these were of costly stones, according to the measures of chiseled stones [gazit], sawed with saws, within and without” (I Kings 7:9). This teaches that chiseled stones are those that have been planed and smoothened. Kefisin refers to small bricks. Leveinim means large bricks.
אֲמַר לֵיהּ רַבָּה בְּרֵיהּ דְּרָבָא לְרַב אָשֵׁי: מִמַּאי דִּגְוִיל אַבְנֵי דְּלָא מְשַׁפְּיָא נִינְהוּ, וְהַאי טֶפַח יַתִּירָא – לְמוּרְשָׁא דְקַרְנָתָא? דִּילְמָא פַּלְגָא דְגָזִית הוּא, וְהַאי טֶפַח יַתִּירָא – לְבֵינֵי אוּרְבֵי הוּא;
Rabba, the son of Rava, said to Rav Ashi: From where do you know that gevil refers to stones that are not planed, and this extra handbreadth that a wall of gevil has compared to what a wall of gazit has is for the protruding edges? That is, a wall of gevil is six handbreadths thick because the stones have not been planed and smoothened, and therefore protrude somewhat outward. Perhaps gevil refers to planed stones that are half the thickness of gazit, namely, just two and a half handbreadths, as compared to gazit, which is five handbreadths thick; and this extra handbreadth in a wall of gevil is for the space between the two rows [urbei]. That is, a wall of gevil is actually two walls of planed stones that are each two and a half handbreadths thick; and the two walls are separated by one handbreadth, which is later filled in with mortar for added strength.
כִּדְקָאָמְרִינַן: כְּפִיסִין – אַרְחֵי, לְבֵינִין – לִיבְנֵי, וְהַאי טֶפַח יַתִּירָא – לְבֵינֵי אוּרְבֵי!
A proof for this explanation can be brought from what we say, i.e., that kefisin are small bricks, whereas leveinim are large bricks, twice the thickness of small bricks. And this extra handbreadth of thickness that a wall of kefisin has compared to what a wall of levinim has is for the space between the two rows of small bricks.
אֲמַר לֵיהּ: וְלִיטַעְמָיךְ, כְּפִיסִין – אַרְחֵי, מְנָלַן? אֶלָּא גְּמָרָא גְּמִירִי לַהּ, גְּוִיל נָמֵי – אַבְנֵי דְּלָא מְשַׁפְּיָא, גְּמָרָא גְּמִירִי לַהּ.
Rav Ashi said to him: And according to your reasoning, from where do we derive that kefisin are small bricks? Rather, the Sages learned this as a tradition. And so too, they learned as a tradition that gevil refers to non-planed stones.
אִיכָּא דְאָמְרִי, אֲמַר לֵיהּ רַב אַחָא בְּרֵיהּ דְּרַב אַוְיָא לְרַב אָשֵׁי: מִמַּאי דְּהַאי כְּפִיסִין – אַרְחֵי נִינְהוּ, וְהַאי טֶפַח יַתִּירָא – לְבֵינֵי אוּרְבֵי? דִּילְמָא מַאי כְּפִיסִין – אַבְנֵי דְּלָא מְשַׁפְּיָין, וְהַאי טֶפַח יַתִּירָא – לְמוּרְשָׁא דְקַרְנָתָא; כִּדְקָאָמְרִינַן: גְּוִיל – אַבְנֵי דְּלָא מְשַׁפְּיָין, גָּזִית – אַבְנֵי דִּמְשַׁפְּיָין, וְהַאי טֶפַח יַתִּירָא – לְמוּרְשָׁא דְקַרְנָתָא!
The Gemara presents a different version of the discussion. There are those who say that Rav Aḥa, son of Rav Avya, said to Rav Ashi: From where do you know that kefisin are small bricks, one-half the width of large bricks, and this extra handbreadth of thickness that a wall of kefisin has compared to what a wall of leveinim has covers the space between the two rows of kefisin? Perhaps you should say what are kefisin? Stones that are not planed, and this extra handbreadth of thickness that a wall of kefisin has in comparison to what a wall of leveinim has is for the protruding edges. And proof for this explanation can be brought from what we say, i.e., that gevil refers to stones that are not planed, whereas gazit means planed stones, and this extra handbreadth of thickness that a wall of gevil has compared to what a wall of gazit has is for the protruding edges.
אֲמַר לֵיהּ: וְלִיטַעְמָיךְ, גְּוִיל – אַבְנֵי דְּלָא מְשַׁפְּיָין, מְנָלַן? אֶלָּא גְּמָרָא גְּמִירִי לַהּ, הָכָא נָמֵי – גְּמָרָא גְּמִירִי לַהּ.
Rav Ashi said to him: And according to your reasoning, from where do we derive that gevil are stones that are not planed? Rather, the Sages learned this as a tradition. Here too, they learned as a tradition that kefisin are small bricks.
אָמַר אַבָּיֵי, שְׁמַע מִינַּהּ: כָּל בֵּינֵי אוּרְבֵי – טֶפַח; הָנֵי מִילֵּי בְּטִינָא, אֲבָל בְּרִיכְסָא בָּעֵי טְפֵי. וְאִיכָּא דְּאָמְרִי: הָנֵי מִילֵּי בְּרִיכְסָא, אֲבָל בְּטִינָא לָא בָּעֵי כּוּלֵּי הַאי.
Abaye said: Learn from it that the space left between the two rows of a wall is always a handbreadth. The Gemara comments: This matter applies only when the two rows of the wall are filled in with mortar. But when they are filled in with gravel [berikhsa], more space is required. And there are those who say that this matter applies only when the two rows of the wall are filled in with gravel. But when mortar is used to fill in the space, not as much space is required, and less than a handbreadth suffices.
לְמֵימְרָא דִּבְגָזִית; דְּכֹל אַרְבַּע אַמּוֹת גּוֹבַהּ, אִי הָוֵי פּוּתְיָא חַמְשָׁא – קָאֵי, אִי לָא – לָא קָאֵי?! וְהָא אַמָּה טְרַקְסִין; דַּהֲוַאי גָּבוֹהַּ תְּלָתִין אַמְּהָתָא, וְלָא הֲוָה פּוּתְיָא אֶלָּא שֵׁית פּוּשְׁכֵי; וְקָם! כֵּיוָן דְּאִיכָּא טֶפַח יַתִּירָא – קָאֵי.
§ The Gemara asks: Is this to say that in the case of a wall of chiseled stone, if for every four cubits of height there are five handbreadths of thickness the wall will stand, and if not it will not stand, as this is the required ratio between a wall’s height and its thickness? But wasn’t there the one-cubit-thick wall separating the Holy of Holies from the Sanctuary of the Temple [amah teraksin] separating the Holy of Holies from the Sanctuary, which was thirty cubits high and its thickness was only six handbreadths and nevertheless stood? The Gemara answers: Since there was an extra handbreadth of thickness, it was able to stand even to such a great height.
וּבְמִקְדָּשׁ שֵׁנִי מַאי טַעְמָא לָא עֲבוּד אַמָּה טְרַקְסִין? כִּי קָאֵי – בִּתְלָתִין קָאֵי, טְפֵי לָא קָאֵי.
The Gemara asks: And what is the reason that in the Second Temple they did not fashion an amah teraksin to separate between the Holy of Holies and the Sanctuary, as they had done in the First Temple? The Gemara answers: When a partition stands even though it is only six handbreadths thick, it is able to remain standing up to thirty cubits in height. But it will not be able to stand if it is more than that height. The Second Temple was taller than the First Temple, and therefore the partition separating the Holy of Holies from the Sanctuary also had to be higher.
וּמְנָלַן דַּהֲוָה גָּבוֹהַּ טְפֵי? דִּכְתִיב: ״גָּדוֹל יִהְיֶה כְּבוֹד הַבַּיִת הַזֶּה הָאַחֲרוֹן מִן הָרִאשׁוֹן״ – רַב וּשְׁמוּאֵל; וְאָמְרִי לַהּ רַבִּי יוֹחָנָן וְרַבִּי אֶלְעָזָר; חַד אָמַר: בְּבִנְיָן, וְחַד אָמַר:
The Gemara comments: And from where do we derive that the Second Temple was taller than the First Temple? As it is written: “The glory of this latter house shall be greater than that of the former” (Haggai 2:9). Rav and Shmuel disagree about the meaning of this verse, and some say it was Rabbi Yoḥanan and Rabbi Elazar who disagreed as to its meaning. One of them said that it means that the Second Temple will be greater in the size of its structure, i.e., taller. And one of them said
בְּשָׁנִים. וְאִיתָא לְהָא וְאִיתָא לְהָא.
that it will be greater in years, meaning that the Second Temple will stand for a longer period of time than the First Temple. And the Gemara comments that this is true and that is true, meaning that the Second Temple was taller than the First Temple and also stood for a longer period of time.
וְנֶיעְבְּדוּ תְּלָתִין אַמִּין בְּבִנְיָן, וְאִידַּךְ נֶיעְבֵּיד פָּרוֹכֶת! כִּי קָאֵי תְּלָתִין אַמְּהָתָא נָמֵי – אַגַּב תִּקְרָה וּמַעֲזִיבָה הֲוָה קָאֵי, בְּלֹא תִּקְרָה וּמַעֲזִיבָה – לָא הֲוָה קָאֵי.
The Gemara asks: If so, if the Second Temple building was taller, then to separate between the Holy of Holies and the Sanctuary in the Second Temple they should have made a wall thirty cubits high and then made a curtain for the rest of the height, the seventy-cubit difference in height between the First and Second Temples. The Gemara answers: This would have been impossible, as even when a thirty-cubit wall that is six handbreadths thick stands, it is due to the ceiling and plaster which attaches it to the ceiling that it stands. But without a ceiling and plaster holding it in place, it does not stand.
וְלֶיעְבֵּיד מָה דְאֶפְשָׁר בְּבִנְיָן, וְלֶיעְבֵּיד אִידַּךְ פָּרוֹכֶת! אָמַר אַבָּיֵי, גְּמִירִי: אִי כּוּלְּהוּ בְּבִנְיָן, אִי כּוּלְּהוּ בְּפָרוֹכֶת. אִי כּוּלְּהוּ בְּבִנְיָן – מִמִּקְדָּשׁ, אִי כּוּלְּהוּ בְּפָרוֹכֶת – מִמִּשְׁכָּן.
The Gemara continues: But they should have made a wall as high as can possibly stand by itself, and then should have made a curtain for the rest of the height. Abaye said: The Sages learned as a tradition that the partition separating the Holy of Holies from the Sanctuary should be built either entirely as a wall or entirely as a curtain. It should be built either entirely as a wall, as is learned from the First Temple, or it should be built entirely as a curtain, as is learned from the Tabernacle. At no time, however, was there a partition that combined a wall and a curtain.
אִיבַּעְיָא לְהוּ: הֵן וְסִידָן, אוֹ דִילְמָא הֵן בְּלֹא סִידָן? אָמַר רַב נַחְמָן בַּר יִצְחָק, מִסְתַּבְּרָא: הֵן וְסִידָן; דְּאִי סָלְקָא דַעְתָּךְ הֵן בְּלֹא סִידָן, לִיתְנְיֵיהּ לְשִׁיעוּרֵיהּ! אֶלָּא לָאו שְׁמַע מִינַּהּ: הֵן וְסִידָן? לָא; לְעוֹלָם אֵימָא לָךְ: הֵן בְּלֹא סִידָן; וְכֵיוָן דְּלָא הָוֵי טֶפַח, לָא תָּנֵי.
§ A dilemma was raised before the Sages: Do the measurements given in the mishna apply to them, the thickness of the materials themselves, and the plaster with which the materials were coated, or perhaps just to them without their plaster? Rav Naḥman bar Yitzḥak said: It is reasonable to say the measurements refer to them and their plaster, as, if it should enter your mind to say they refer to them without their plaster, then the tanna should have taught the measurements of the plaster as well. Rather, isn’t it correct to conclude from here that the measurements refer to them and their plaster? The Gemara rejects this conclusion: No, actually I could say to you that they apply to them without their plaster, and since the plaster does not have the thickness of one handbreadth the tanna did not teach such a small measurement.
וְהָא קָתָנֵי: בִּלְבֵינִין – זֶה נוֹתֵן טֶפַח וּמֶחֱצָה וְזֶה נוֹתֵן טֶפַח וּמֶחֱצָה! הָתָם חֲזִי לְאִיצְטְרוֹפֵי.
The Gemara asks: But doesn’t the tanna teach with regard to bricks that this one provides one and a half handbreadths, and that one provides one and a half handbreadths? Evidently, the tanna lists even an amount less than one handbreadth. The Gemara answers: There mention is made of half-handbreadths because they are fit to be combined into a full handbreadth.
תָּא שְׁמַע: הַקּוֹרָה שֶׁאָמְרוּ – רְחָבָה כְּדֵי לְקַבֵּל אָרִיחַ, וְהָאָרִיחַ – חֲצִי לְבֵינָה שֶׁל שְׁלֹשָׁה טְפָחִים!
The Gemara suggests: Come and hear a solution to the question, from a mishna (Eiruvin 13b) in which it is taught: The cross beam, which the Sages stated may be used to render an alleyway fit for one to carry within it on Shabbat, must be wide enough to receive and hold a small brick. And this small brick is half a large brick, the width of which is three handbreadths. That mishna is referring to a brick without the plaster.
הָתָם בְּרַבְרְבָתָא. דַּיְקָא נָמֵי, דְּקָתָנֵי: ״שֶׁל שְׁלֹשָׁה טְפָחִים״, מִכְלָל דְּאִיכָּא זוּטְרָא; שְׁמַע מִינַּהּ.
The Gemara answers: There, the mishna in Eiruvin is referring to large bricks that measure three full handbreadths, whereas here the mishna is referring to bricks that measure slightly less than three handbreadths, and the measurement of three handbreadths includes the plaster with which they are coated. The Gemara comments: The language of the mishna there is also precise, as it teaches about a brick of three handbreadths, from which one can conclude by inference that there exists also a smaller-sized brick. The Gemara affirms: Learn from here that the mishna there is referring to large bricks.
אָמַר רַב חִסְדָּא: לֹא לִיסְתּוֹר אִינִישׁ בֵּי כְנִישְׁתָּא, עַד דְּבָנֵי בֵּי כְנִישְׁתָּא אַחֲרִיתִי. אִיכָּא דְאָמְרִי: מִשּׁוּם פְּשִׁיעוּתָא, וְאִיכָּא דְאָמְרִי: מִשּׁוּם צַלּוֹיֵי.
§ Rav Ḥisda says: A person may not demolish a synagogue until he first builds another synagogue to take its place. There are those who say that the reason for this halakha is due to potential negligence, lest he fail to build a new structure after the old one has been razed. And there are those who say that the reason for this halakha is due to the disruption of prayer, for in the meantime there will be nowhere to pray.
מַאי בֵּינַיְיהוּ? אִיכָּא בֵּינַיְיהוּ דְּאִיכָּא בֵּי כְנִישְׁתָּא אַחֲרִיתִי. מָרִימָר וּמַר זוּטְרָא סָתְרִי וּבָנוּ בֵּי קַיְיטָא בְּסִיתְווֹא, וּבָנוּ בֵּי סִיתְווֹא בְּקַיְיטָא.
The Gemara asks: What is the practical difference between these two explanations? The Gemara answers that there is a difference between them in a situation where there is another synagogue. Even though the community has an alternative place to pray there is still a concern that the new synagogue will never get built. It is related that Mareimar and Mar Zutra demolished and built a summer synagogue in the winter, and, in like manner, they built a winter synagogue in the summer, so that the community would never be left without a synagogue.
אֲמַר לֵיהּ רָבִינָא לְרַב אָשֵׁי: גְּבוּ זוּזֵי וּמַחֲתִי, מַאי? אֲמַר לֵיהּ: דִּילְמָא מִיתְרְמֵי לְהוּ פִּדְיוֹן שְׁבוּיִים, וְיָהֲבִי לְהוּ.
Ravina said to Rav Ashi: What is the halakha if money for the construction of a new synagogue has already been collected and it rests before us for that purpose? Is it then permitted to demolish the old synagogue before building the new one? Rav Ashi said to him: Even if the money has been collected there is still concern that perhaps an opportunity for redeeming captives will present itself, and they will hand over the money for that urgent requirement, and the community will be left without a synagogue.
שְׁרִיגִי לִיבְנֵי, וְהָדְרִי הוּדְרֵי, וּמַחֲתִי כְּשׁוּרֵי, מַאי? אֲמַר לֵיהּ: זִמְנִין דְּמִתְרְמֵי לְהוּ פִּדְיוֹן שְׁבוּיִים, מְזַבְּנִי וְיָהֲבִי לְהוּ. אִי הָכִי, אֲפִילּוּ בָּנוּ נָמֵי! אֲמַר לֵיהּ: דִּירְתֵיהּ דְּאִינָשֵׁי לָא מְזַבְּנִי.
Ravina continues: What is the halakha if the bricks to be used for the construction of the new synagogue are piled up, the boards are prepared, and the beams are ready? Is it permitted to demolish the old synagogue before building the new one? Rav Ashi said to him: Even so, sometimes an opportunity for redeeming captives will present itself, and they will sell the building materials and hand over the proceeds for this purpose. Ravina raises an objection: If so, that is, if you are concerned that they will sell the materials to redeem captives, then even in a case where they already built the synagogue there should be a concern that they might come to sell the structure for that purpose, and therefore one should never be permitted to destroy an old synagogue. Rav Ashi said to him: People do not sell their residences, and certainly not their synagogues.
וְלָא אֲמַרַן אֶלָּא דְּלָא חָזֵי בָּהּ תִּיוְהָא, אֲבָל חָזֵי בָּהּ תִּיוְהָא – סָתְרִי וּבָנֵי. כִּי הָא דְּרַב אָשֵׁי חֲזָא בָּהּ תִּיוְהָא בִּכְנִישְׁתָּא דְּמָתָא מַחְסֵיָא, סַתְרֵיהּ וְעַיֵּיל לְפוּרְיֵיהּ לְהָתָם, וְלָא אַפְּקֵיהּ עַד דִּמְתַקֵּין לֵיהּ שְׁפִיכֵי.
The Gemara comments: And we said that an old synagogue must not be razed before its replacement is built only in a case where cracks are not seen in the old synagogue. But if cracks are seen they may first demolish the old synagogue and then build the new one. This is like the incident involving Rav Ashi, who saw cracks in the synagogue in his town of Mata Meḥasya and immediately demolished it. He then brought his bed in there, to the building site, so that there should be no delays in the construction, as he himself required shelter from the rain, and he did not remove his bed from there until they finished building the synagogue and even affixed drainpipes to the structure.
וּבָבָא בֶּן בּוּטָא, הֵיכִי אַסְּבֵיהּ לֵיהּ עֵצָה לְהוֹרְדוֹס לְמִיסְתְּרֵיהּ לְבֵית הַמִּקְדָּשׁ? וְהָאָמַר רַב חִסְדָּא: לָא לִיסְתּוֹר אִינִישׁ בֵּי כְנִישְׁתָּא עַד דְּבָנֵי בֵּי כְנִישְׁתָּא אַחְרִיתָא! אִי בָּעֵית אֵימָא: תִּיוְהָא חֲזָא בֵּיהּ, אִיבָּעֵית אֵימָא: מַלְכוּתָא שָׁאנֵי, דְּלָא הָדְרָא בֵּיהּ; דְּאָמַר שְׁמוּאֵל, אִי אָמַר מַלְכוּתָא: ״עָקַרְנָא טוּרֵי״ – עָקַר טוּרֵי וְלָא הָדַר בֵּיהּ.
The Gemara asks: How could Bava ben Buta have advised Herod to raze the Temple and build another in its place, as will be described later? But doesn’t Rav Ḥisda say that a person must not demolish a synagogue unless he first builds another synagogue to take its place? The Gemara answers: If you wish, say that he saw cracks in the old Temple structure. And if you wish, say that actions taken by the government are different, as the government does not go back on its decisions. Therefore, there is no need to be concerned about negligence, as there is in the case of ordinary people. As Shmuel says: If the government says it will uproot mountains, it will uproot mountains and not retract its word.
הוֹרְדוֹס עַבְדָּא דְּבֵית חַשְׁמוֹנַאי הֲוָה. נָתַן עֵינָיו בְּאוֹתָהּ תִּינוֹקֶת. יוֹמָא חַד, שְׁמַע הָהוּא גַּבְרָא בַּת קָלָא דְּאָמַר: כָּל עַבְדָּא דְּמָרֵיד הַשְׁתָּא, מַצְלַח. קָם קַטְלִינְהוּ לְכוּלְּהוּ מָרְוָתֵיהּ, וְשַׁיְּירַהּ לְהַהִיא יָנוֹקְתָּא. כִּי חֲזָת הָהִיא יָנוֹקְתָּא דְּקָא בָּעֵי לְמִינְסְבַהּ, סְלִיקָא לְאִיגָּרָא, וּרְמָא קָלָא אֲמַרָה: ״כֹּל מַאן דְּאָתֵי וְאָמַר: מִבֵּית חַשְׁמוֹנַאי קָאָתֵינָא – עַבְדָּא הוּא, דְּלָא אִישְׁתְּיַירָא מִינַּיְיהוּ אֶלָּא הַהִיא יָנוֹקְתָּא, וְהַהִיא יָנוֹקְתָּא נְפַלָה מֵאִיגָּרָא לְאַרְעָא״.
§ The Gemara elaborates on the episode involving Bava ben Buta. Herod was a slave in the house of the Hasmoneans. He set his eyes upon a certain young girl from the house of the Hasmoneans. One day that man, Herod, heard a Divine Voice that said: Any slave who rebels now will succeed. He rose up and killed all his masters, but spared that girl. When that girl saw that he wanted to marry her, she went up to the roof and raised her voice, and said: Whoever comes and says: I come from the house of the Hasmoneans, is a slave, since only that girl, i.e., I, remained from them. And that girl fell from the roof to the ground and died.
טַמְנַהּ שְׁבַע שְׁנִין בְּדוּבְשָׁא. אִיכָּא דְּאָמְרִי: בָּא עָלֶיהָ, אִיכָּא דְאָמְרִי: לָא בָּא עָלֶיהָ. דְּאָמְרִי לַהּ בָּא עָלֶיהָ, הָא דְּטַמְנַהּ – לְיַתּוֹבֵיהּ לְיִצְרֵיהּ. וּדְאָמְרִי לַהּ לֹא בָּא עָלֶיהָ, הַאי דְּטַמְנַהּ – כִּי הֵיכִי דְּנֵאמְרוּ: בַּת מֶלֶךְ נְסַב.
It is related that Herod preserved the girl’s body in honey for seven years to prevent it from decaying. There are those who say that he engaged in necrophilia with her corpse and there are those who say he did not engage in necrophilia with her corpse. According to those who say he engaged in necrophilia with her corpse, the reason that he preserved her body was to gratify his carnal desires. And according to those who say he did not engage in necrophilia with her corpse, the reason that he preserved her body was so that people would say he married a king’s daughter.
אֲמַר: מַאן דָּרֵישׁ ״מִקֶּרֶב אַחֶיךָ תָּשִׂים עָלֶיךָ מֶלֶךְ״? רַבָּנַן. קָם קַטְלִינְהוּ לְכוּלְּהוּ רַבָּנַן, שַׁבְקֵיהּ לְבָבָא בֶּן בּוּטָא לְמִשְׁקַל עֵצָה מִנֵּיהּ.
Herod said to himself: Who expounds the verse: “One from among your brothers you shall set as king over you” (Deuteronomy 17:15) as meaning that he who is appointed as king must come from a Jewish family and cannot be an emancipated slave or a convert? It is the Sages who expound the verse in this manner, insisting that a king must have Jewish roots. He then rose up and killed all the Sages, but spared Bava ben Buta in order to take counsel with him.