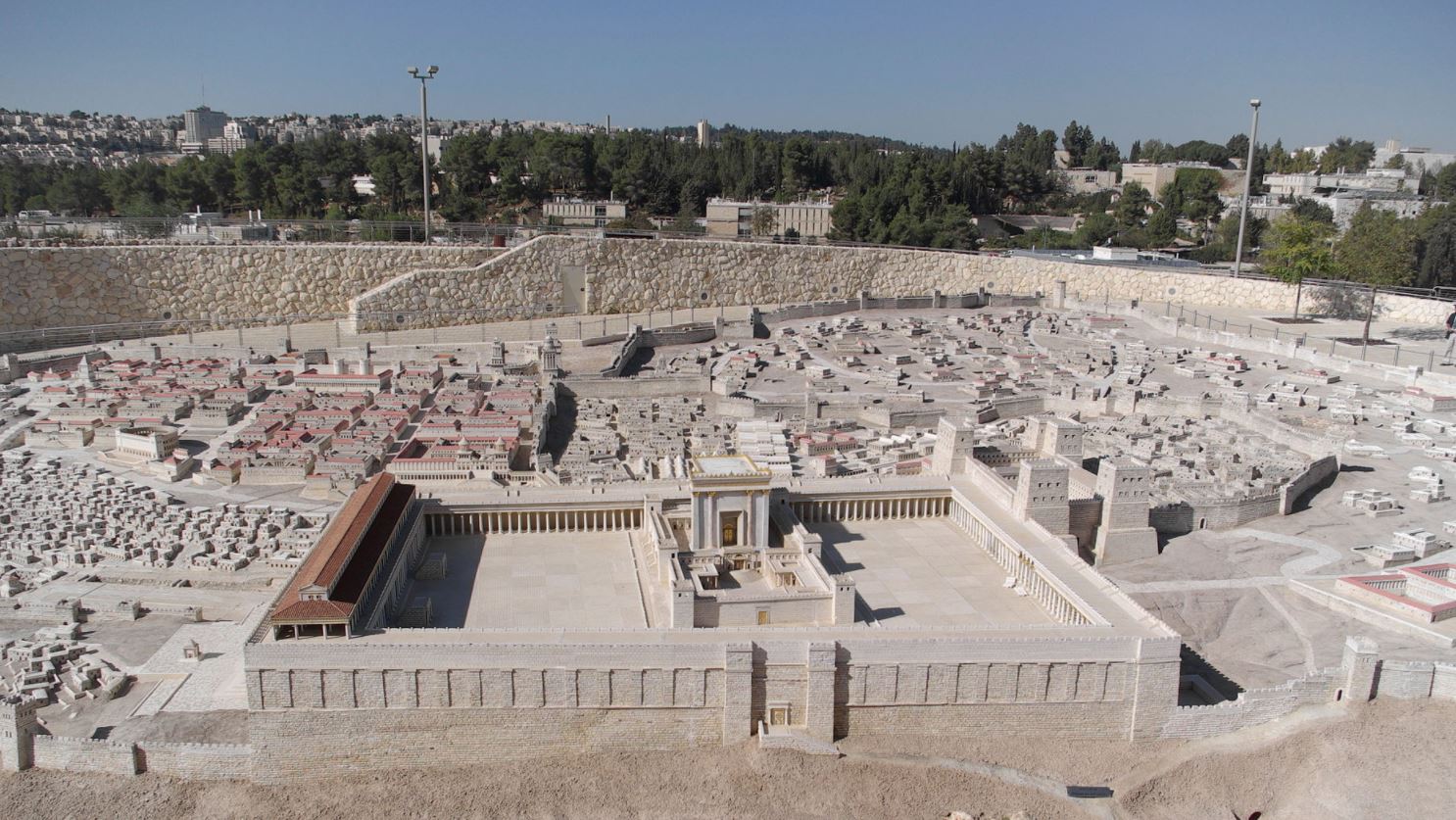
Pesachim 66
אָמַר לוֹ רַבִּי עֲקִיבָא, אוֹ חִלּוּף: מָה אִם הַזָּאָה שֶׁהִיא מִשּׁוּם שְׁבוּת — אֵינָהּ דּוֹחָה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת, שְׁחִיטָה שֶׁהִיא מִשּׁוּם מְלָאכָה — אֵינוֹ דִּין שֶׁלֹּא תִּדְחֶה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת?! אָמַר לוֹ רַבִּי אֱלִיעֶזֶר: עֲקִיבָא, עָקַרְתָּ מַה שֶּׁכָּתוּב בַּתּוֹרָה: ״בְּמוֹעֲדוֹ״, בֵּין בַּחוֹל בֵּין בַּשַּׁבָּת.
Rabbi Akiva said to Rabbi Eliezer: Or perhaps we can reverse the order of your argument and say the opposite: If, as we know by accepted tradition, sprinkling the purifying water on Shabbat, which is prohibited only due to rabbinic decree, does not override Shabbat, then with regard to slaughter, which is prohibited as a biblically prohibited labor, is it not right that it should not override Shabbat? Therefore, it should be prohibited to slaughter the Paschal lamb when the eve of Passover occurs on Shabbat. Rabbi Eliezer said to him: Akiva, how can you say this? You have thus uprooted what is written in the Torah: “Let the children of Israel offer the Paschal lamb in its appointed time” (Numbers 9:2); the phrase “at its appointed time” indicates that the offering must be brought on that day, whether it is a weekday or Shabbat.
אָמַר לוֹ: רַבִּי, הָבֵא לִי מוֹעֵד לְאֵלּוּ, כְּמוֹעֵד לַשְּׁחִיטָה. כְּלָל אָמַר רַבִּי עֲקִיבָא: כׇּל מְלָאכָה שֶׁאֶפְשָׁר לַעֲשׂוֹתָהּ מֵעֶרֶב שַׁבָּת — אֵינָהּ דּוֹחָה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת. שְׁחִיטָה, שֶׁאִי אֶפְשָׁר לַעֲשׂוֹתָהּ מֵעֶרֶב שַׁבָּת — דּוֹחָה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת.
Rabbi Akiva said to Rabbi Eliezer: My teacher, bring me an appointed time stated in the Torah for these tasks, namely, carrying the animal or bringing it from outside the Shabbat limits, like the appointed time stated with respect to slaughter. The Paschal lamb must be slaughtered on the fourteenth of Nisan, but there is no fixed time when the animal must be brought to the Temple, and it is therefore possible to transport it before Shabbat. Rabbi Akiva stated a principle: Any prohibited labor required for the offering of the sacrifice that can be performed on the eve of Shabbat does not override Shabbat; slaughter, which cannot be performed on the eve of Shabbat, overrides Shabbat.
גְּמָ׳ תָּנוּ רַבָּנַן: הֲלָכָה זוֹ נִתְעַלְּמָה מִבְּנֵי בְתִירָא. פַּעַם אַחַת חָל אַרְבָּעָה עָשָׂר לִהְיוֹת בְּשַׁבָּת, שָׁכְחוּ וְלֹא יָדְעוּ אִם פֶּסַח דּוֹחֶה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת אִם לָאו. אָמְרוּ: כְּלוּם יֵשׁ אָדָם שֶׁיּוֹדֵעַ אִם פֶּסַח דּוֹחֶה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת אִם לָאו? אָמְרוּ לָהֶם: אָדָם אֶחָד יֵשׁ שֶׁעָלָה מִבָּבֶל וְהִלֵּל הַבַּבְלִי שְׁמוֹ, שֶׁשִּׁימֵּשׁ שְׁנֵי גְּדוֹלֵי הַדּוֹר שְׁמַעְיָה וְאַבְטַלְיוֹן, וְיוֹדֵעַ אִם פֶּסַח דּוֹחֶה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת אִם לָאו. שָׁלְחוּ וְקָרְאוּ לוֹ, אָמְרוּ לוֹ: כְּלוּם אַתָּה יוֹדֵעַ אִם הַפֶּסַח דּוֹחֶה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת אִם לָאו? אָמַר לָהֶם: וְכִי פֶּסַח אֶחָד יֵשׁ לָנוּ בַּשָּׁנָה שֶׁדּוֹחֶה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת? וַהֲלֹא הַרְבֵּה יוֹתֵר מִמָּאתַיִם פְּסָחִים יֵשׁ לָנוּ בַּשָּׁנָה שֶׁדּוֹחִין אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת.
GEMARA: The Sages taught a baraita with regard to the basic halakha governing the eve of Passover that occurs on Shabbat: This law was forgotten by the sons of Beteira, who were the leaders of their generation. The fourteenth of Nisan once occurred on Shabbat, and they forgot and did not know whether the Paschal lamb overrides Shabbat or not. They said: Is there any person who knows whether the Paschal lamb overrides Shabbat or not? They said to them: There is a certain man in Jerusalem who came up from Babylonia, and Hillel the Babylonian is his name. At one point, he served the two most eminent scholars of the generation, Shemaya and Avtalyon, and he certainly knows whether the Paschal lamb overrides Shabbat or not. The sons of Beteira sent messengers and called for him. They said to him: Do you know whether the Paschal lamb overrides Shabbat or not? He said to them: Have we but one Paschal lamb during the year that overrides Shabbat? Do we not have many more than two hundred Paschal lambs, i.e., sacrifices, during the year that override Shabbat?
אָמְרוּ לוֹ: מִנַּיִן לְךָ? אָמַר לָהֶם: נֶאֱמַר ״מוֹעֲדוֹ״ בַּפֶּסַח, וְנֶאֱמַר ״מוֹעֲדוֹ״ בַּתָּמִיד: מָה ״מוֹעֲדוֹ״ הָאָמוּר בַּתָּמִיד דּוֹחֶה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת, אַף ״מוֹעֲדוֹ״ הָאָמוּר בַּפֶּסַח דּוֹחֶה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת.
They said to him: From where do you know this? He said to them: “Its appointed time” is stated with regard to the Paschal lamb and “its appointed time” is also stated with regard to the daily offering, for the verse says: “Command the children of Israel and say to them, My offering, the provision of My sacrifice made with fire, for a sweet savor to Me, shall you observe to offer Me at its appointed time” (Numbers 28:2). From here we learn that the daily offering is brought even on Shabbat. Thus, the daily morning and afternoon offerings are brought on more than fifty Shabbatot over the course of the year, and two sheep are offered every Shabbat as additional offerings, for a total of more than two hundred sacrifices a year that override Shabbat. Just as the expression “its appointed time,” which is stated with regard to the daily offering, indicates that it overrides Shabbat, so too “its appointed time,” which is stated with regard to the Paschal lamb, indicates that it overrides Shabbat.
וְעוֹד, קַל וָחוֹמֶר הוּא: וּמָה תָּמִיד שֶׁאֵין עָנוּשׁ כָּרֵת דּוֹחֶה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת, פֶּסַח שֶׁעָנוּשׁ כָּרֵת — אֵינוֹ דִּין שֶׁדּוֹחֶה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת.
And furthermore, it is an a fortiori inference: If the daily offering, the neglect of which is not punishable by karet, overrides Shabbat, is it not right that the Paschal lamb, the neglect of which is punishable by karet, should override Shabbat?
מִיָּד הוֹשִׁיבוּהוּ בָּרֹאשׁ, וּמִינּוּהוּ נָשִׂיא עֲלֵיהֶם, וְהָיָה דּוֹרֵשׁ כׇּל הַיּוֹם כּוּלּוֹ בְּהִלְכוֹת הַפֶּסַח. הִתְחִיל מְקַנְטְרָן בִּדְבָרִים. אָמַר לָהֶן: מִי גָּרַם לָכֶם שֶׁאֶעְלֶה מִבָּבֶל וְאֶהְיֶה נָשִׂיא עֲלֵיכֶם — עַצְלוּת שֶׁהָיְתָה בָּכֶם, שֶׁלֹּא שִׁמַּשְׁתֶּם שְׁנֵי גְּדוֹלֵי הַדּוֹר, שְׁמַעְיָה וְאַבְטַלְיוֹן.
After Hillel brought these proofs, they immediately seated him at the head and appointed him Nasi over them, and he expounded the laws of Passover that entire day. In the course of his teaching, he began rebuking them [mekanteran] them with words. He said to them: What caused this to happen to you, that I should come up from Babylonia and become Nasi over you? It was the laziness in you that you did not serve the two most eminent scholars of the generation living in Eretz Yisrael, Shemaya and Avtalyon.
אָמְרוּ לוֹ: רַבִּי, שָׁכַח וְלֹא הֵבִיא סַכִּין מֵעֶרֶב שַׁבָּת, מַהוּ? אָמַר לָהֶן: הֲלָכָה זוֹ שָׁמַעְתִּי וְשָׁכַחְתִּי, אֶלָּא הַנַּח לָהֶן לְיִשְׂרָאֵל, אִם אֵין נְבִיאִים הֵן — בְּנֵי נְבִיאִים הֵן.
They said to Hillel: Our teacher, if one forgot and did not bring a knife on the eve of Shabbat and cannot slaughter his Paschal lamb, what is the law? Since he could have brought the knife before Shabbat, he cannot bring it on Shabbat; but what should he do in this situation? He said to them: I once heard this halakha from my teachers but I have forgotten it. But leave it to the Jewish people; if they are not prophets to whom God has revealed His secrets, they are the sons of prophets, and will certainly do the right thing on their own.
לְמָחָר, מִי שֶׁפִּסְחוֹ טָלֶה — תּוֹחֲבוֹ בְּצַמְרוֹ, מִי שֶׁפִּסְחוֹ גְּדִי — תּוֹחֲבוֹ בֵּין קַרְנָיו. רָאָה מַעֲשֶׂה וְנִזְכַּר הֲלָכָה, וְאָמַר: כָּךְ מְקוּבְּלַנִי מִפִּי שְׁמַעְיָה וְאַבְטַלְיוֹן.
The next day, on Shabbat that was the eve of Passover, one whose Paschal offering was a lamb took the knife and stuck it in its wool; and one whose Paschal offering was a goat, which does not have wool, stuck it between its horns. Hillel saw the incident and remembered the halakha that he had once learned and said: This is the tradition I received from the mouths of Shemaya and Avtalyon, meaning that this is in fact the proper course of action. This concludes the text of the baraita and the Gemara will begin to elucidate it.
אָמַר מָר: נֶאֱמַר ״מוֹעֲדוֹ״ בַּפֶּסַח, וְנֶאֱמַר ״מוֹעֲדוֹ״ בְּתָמִיד, מָה ״מוֹעֲדוֹ״ הָאָמוּר בַּתָּמִיד דּוֹחֶה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת, אַף ״מוֹעֲדוֹ״ הָאָמוּר בַּפֶּסַח דּוֹחֶה שַׁבָּת. וְתָמִיד גּוּפֵיהּ מְנָלַן דְּדָחֵי שַׁבָּת? אִילֵּימָא מִשּׁוּם דִּכְתִיב בֵּיהּ ״בְּמוֹעֲדוֹ״ — פֶּסַח נָמֵי הָא כְּתִיב בֵּיהּ ״מוֹעֲדוֹ״!
The Master said above: “Its appointed time” is stated with regard to the Paschal lamb and “its appointed time” is stated with regard to the daily offering. Just as “its appointed time,” which is stated with regard to the daily offering, indicates that it overrides Shabbat, so too “its appointed time,” which is stated with regard to the Paschal lamb, indicates that it overrides Shabbat. And from where do we derive that the daily offering itself overrides Shabbat? If we say because “in its appointed time” is written in its regard, “in its appointed time” is also written with regard to the Paschal lamb. Were it possible to derive from this expression that the sacrifice is offered even on Shabbat, it would not be necessary to derive the law governing the Paschal lamb from a verbal analogy between the daily offering and the Paschal lamb.
אֶלָּא ״מוֹעֲדוֹ״ לָא מַשְׁמַע לֵיהּ. הָכָא נָמֵי ״מוֹעֲדוֹ״ לָא מַשְׁמַע לֵיהּ. אֶלָּא אָמַר קְרָא: ״עוֹלַת שַׁבָּת בְּשַׁבַּתּוֹ עַל עוֹלַת הַתָּמִיד״ — מִכְּלָל [עוֹלָה] דְּתָמִיד קְרֵבָה בְּשַׁבָּת.
Rather, you must conclude that the expression “its appointed time,” which is stated with regard to the Paschal lamb, does not indicate to Hillel that the Torah was so particular about the timing of the Paschal lamb that its slaughter overrides Shabbat. Here too, with regard to the daily offering, you must say that “its appointed time” does not indicate to him that it is brought on Shabbat, and so this expression is not the source of this law. Rather, the law is derived from the verse that states: “The burnt-offering of Shabbat on its Shabbat, beside the continual burnt-offering and its libation” (Numbers 28:10), from which it may be inferred that the daily burnt-offering is brought even on Shabbat.
אָמַר מָר: וְעוֹד קַל וָחוֹמֶר, וּמָה תָּמִיד שֶׁאֵין עָנוּשׁ כָּרֵת דּוֹחֶה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת, פֶּסַח שֶׁעָנוּשׁ כָּרֵת — אֵינוֹ דִּין שֶׁדּוֹחֶה אֶת הַשַּׁבָּת. אִיכָּא לְמִיפְרַךְ: מָה לְתָמִיד שֶׁכֵּן תָּדִיר וְכָלִיל. קַל וָחוֹמֶר אֲמַר לְהוּ בְּרֵישָׁא וּפַרְכוּהּ, וַהֲדַר אֲמַר לְהוּ גְּזֵירָה שָׁוָה.
The Gemara raises another question: The Master said in that same baraita: And furthermore, it is an a fortiori inference: If the daily offering, the neglect of which is not punishable by karet, overrides Shabbat, is it not right that the Paschal lamb, the neglect of which is punishable by karet, should override Shabbat? The Gemara points out that there is room to refute the logic of this argument: What is unique about the daily offering that enables it to override Shabbat? That it is frequent, and something that is frequent always takes precedence; and also that it is totally consumed on the altar, unlike the Paschal lamb, most of which is eaten by human beings. The Gemara explains that this is what happened: Hillel first told them the a fortiori inference, but they refuted it and proved that it was not reliable, as explained above; and then he told them the verbal analogy, and a verbal analogy is based on an oral tradition originating from Moses at Sinai and must be accepted.
וְכִי מֵאַחַר דְּגָמַר גְּזֵירָה שָׁוָה, קַל וָחוֹמֶר לְמָה לִי? אֶלָּא לְדִידְהוּ קָאָמַר לְהוּ: בִּשְׁלָמָא גְּזֵירָה שָׁוָה לָא גָּמְרִיתוּ, דְּאֵין אָדָם דָּן גְּזֵירָה שָׁוָה מֵעַצְמוֹ. אֶלָּא קַל וָחוֹמֶר, דְּאָדָם דָּן מֵעַצְמוֹ, אִיבְּעִי לְכוּ לְמֵידָן! אֲמַרוּ לֵיהּ: קַל וָחוֹמֶר פְּרִיכָא הוּא.
The Gemara asks: But since Hillel learned this verbal analogy from his teachers, why do I need an a fortiori inference? Why did he add a logical argument of his own if he had an explicit verbal tradition that this was the halakha? The Gemara answers: Rather, he said it for them, to show that they had not sufficiently exerted themselves in clarifying this halakha: Granted, you did not learn the verbal analogy on your own, because you acted according to the principle that one may not expound a verbal analogy on one’s own. Since there is no limit to the laws that one can extract using this method of derivation, such a derivation is only legitimate if it has been transmitted as part of the oral tradition, and apparently they did not learn this verbal analogy from their teachers. But an a fortiori inference, which one can derive on one’s own, you should have derived and you would then have known how to resolve this question. They said to him: It is a faulty a fortiori inference, as we have shown that it can be easily refuted.
אָמַר מָר: לְמָחָר מִי שֶׁפִּסְחוֹ טָלֶה — תּוֹחֵב לוֹ בְּצַמְרוֹ, גְּדִי — תּוֹחֵב לוֹ בֵּין קַרְנָיו.
The Master said further in the baraita: The next day, one whose Paschal offering was a lamb stuck the knife in its wool, and one whose Paschal offering was a goat stuck it between its horns so as to avoid carrying the knife on Shabbat.
וְהָא קָא עָבֵיד עֲבוֹדָה בְּקָדָשִׁים! כְּהִלֵּל. דְּתַנְיָא, אָמְרוּ עָלָיו עַל הִלֵּל: מִיָּמָיו לֹא מָעַל אָדָם בְּעוֹלָתוֹ. אֶלָּא מְבִיאָהּ חוּלִּין לָעֲזָרָה וּמַקְדִּישָׁהּ, וְסוֹמֵךְ יָדוֹ עָלֶיהָ וְשׁוֹחֲטָהּ.
But surely he did work with consecrated animals, using the lambs and goats that had been consecrated as sacrifices to transport the knife, and it is forbidden to make use of consecrated animals. The Gemara answers that the person acted here in accordance with the opinion of Hillel, as it was taught in a baraita: They said about Hillel that no one ever misused his burnt-offering. How did he ensure this? He was careful not to consecrate the animal in advance, but rather he would bring it in an unconsecrated state to the Temple courtyard and there he would consecrate it, and then immediately he would place his hand on its head and slaughter it. On that day, those who used their Paschal lambs and goats to transport knives consecrated their animals only after they arrived in the Temple courtyard.
פֶּסַח בְּשַׁבָּת הֵיכִי מָצֵי מַקְדֵּישׁ לֵיהּ, וְהָתְנַן: אֵין מַקְדִּישִׁין וְאֵין מַעֲרִיכִין וְאֵין מַחְרִימִין וְאֵין מַגְבִּיהִין תְּרוּמָה וּמַעַשְׂרוֹת. כׇּל אֵלּוּ בְּיוֹם טוֹב אָמְרוּ, קַל וָחוֹמֶר בַּשַּׁבָּת!
The Gemara asks: If so, how could they consecrate the Paschal offerings that year when Passover eve occurred on Shabbat? Didn’t we learn in a mishna: One may not consecrate animals, take a valuation vow, consecrate objects for use by the priests or the Temple, or separate terumot and tithes. They stated all of these prohibitions with regard to a Festival, and it is an a fortiori inference that these activities are prohibited on Shabbat as well, for the Sages decreed that one should not engage in these activities because they are similar to business transactions and weekday activities.
הָנֵי מִילֵּי בְּחוֹבוֹת שֶׁאֵין קָבוּעַ לָהֶן זְמַן. אֲבָל בְּחוֹבוֹת שֶׁקָּבוּעַ לָהֶן זְמַן — מַקְדִּישִׁין. דְּאָמַר רַבִּי יוֹחָנָן: מַקְדִּישׁ אָדָם אֶת פִּסְחוֹ בְּשַׁבָּת וַחֲגִיגָתוֹ בְּיוֹם טוֹב.
The Gemara answers: This prohibition of consecrating an animal as a sacrifice on Shabbat or a Festival applies only to obligatory sacrifices that do not have a set time to be brought. But obligatory sacrifices that have a set time, such as the Paschal lamb, one may consecrate even on Shabbat. For Rabbi Yoḥanan said: A person may consecrate his Paschal lamb on Shabbat and his Festival peace-offering on the Festival. Since these sacrifices must be brought on a specific day, they may be consecrated on that day even when it is Shabbat or a Festival, as the Sages did not uphold their decree in this circumstance.
וַהֲלֹא מְחַמֵּר! מְחַמֵּר כִּלְאַחַר יָד: מְחַמֵּר כִּלְאַחַר יָד נָמֵי נְהִי דְּאִיסּוּרָא דְּאוֹרָיְיתָא לֵיכָּא אִיסּוּרָא מִדְּרַבָּנַן מִיהָא אִיכָּא.
The Gemara asks: But is he not driving a laden animal? One who leads a lamb that is carrying a knife is considered as one who is driving a laden animal, which is prohibited on Shabbat. The Gemara answers: It is driving a laden animal in an unusual manner, as a lamb is not typically used to carry loads. The Gemara asks: Even driving a laden animal in an unusual manner is problematic; granted that there is no prohibition by Torah law, but there is at least a rabbinic prohibition. When one performs a prohibited act on Shabbat in an unusual manner, he does not transgress a Torah prohibition, but nonetheless, he violates a rabbinic prohibition.
הַיְינוּ דְּקָא בָּעֵי מִינֵּיהּ: דָּבָר שֶׁיֵּשׁ לוֹ הֶיתֵּר מִן הַתּוֹרָה, וּדְבַר שְׁבוּת עוֹמֵד לְפָנָיו, לְעׇקְרוֹ כִּלְאַחַר יָד בִּמְקוֹם מִצְוָה מַאי? אָמַר לָהֶן: הֲלָכָה זוֹ שָׁמַעְתִּי וְשָׁכַחְתִּי, אֶלָּא הַנִּיחוּ לָהֶן לְיִשְׂרָאֵל, אִם אֵין נְבִיאִים הֵן — בְּנֵי נְבִיאִים הֵן.
The Gemara answers: This is precisely what the sons of Beteira asked Hillel: If there is an act that is permitted by Torah law, and a rabbinic decree stands before it and disallows it, what is the law with regard to the permissibility of uprooting the rabbinic decree in an unusual manner, in a situation in which one does so in order to fulfill a mitzva? Bringing the sacrifice is a mitzva, whereas leading the animal while it carries a knife is an unusual way of violating a rabbinic prohibition. Is this permitted? Hillel said to them: I once heard this halakha but I have forgotten it. But leave it to the Jewish people and rely on them to come up with a solution on their own, for if they are not prophets, they are the sons of prophets.
אָמַר רַב יְהוּדָה אָמַר רַב: כׇּל הַמִּתְיַהֵר, אִם חָכָם הוּא — חׇכְמָתוֹ מִסְתַּלֶּקֶת מִמֶּנּוּ, אִם נָבִיא הוּא — נְבוּאָתוֹ מִסְתַּלֶּקֶת מִמֶּנּוּ. אִם חָכָם הוּא חׇכְמָתוֹ מִסְתַּלֶּקֶת מִמֶּנּוּ — מֵהִלֵּל, דְּאָמַר מָר הִתְחִיל מְקַנְטְרָן בִּדְבָרִים, וְקָאָמַר לְהוּ: הֲלָכָה זוֹ שָׁמַעְתִּי וְשָׁכַחְתִּי. אִם נָבִיא הוּא נְבוּאָתוֹ מִסְתַּלֶּקֶת מִמֶּנּוּ — מִדְּבוֹרָה, דִּכְתִיב: ״חָדְלוּ פְרָזוֹן בְּיִשְׂרָאֵל חָדֵלּוּ עַד שַׁקַּמְתִּי דְּבוֹרָה שַׁקַּמְתִּי אֵם בְּיִשְׂרָאֵל וְגוֹ׳״, וּכְתִיב: ״עוּרִי עוּרִי דְּבוֹרָה עוּרִי עוּרִי דַּבְּרִי שִׁיר וְגוֹ׳״.
With regard to the incident with Hillel, Rav Yehuda said that Rav said: Anyone who acts haughtily, if he is a Torah scholar, his wisdom departs from him; and if he is a prophet, his prophecy departs from him. The Gemara explains: That if he is a Torah scholar, his wisdom departs from him is learned from Hillel, for the Master said in this baraita: Hillel began to rebuke them with words. Because he acted haughtily, he ended up saying to them: I once heard this halakha, but I have forgotten it, as he was punished for his haughtiness by forgetting the law. That if he is a prophet his prophecy departs from him is learned from Deborah, as it is written: “The villagers ceased, they ceased in Israel, until I, Deborah, arose, I arose a mother in Israel” (Judges 5:7). For these words of self-glorification, Deborah was punished with a loss of her prophetic spirit, as it is written later that it was necessary to say to her: “Awake, awake, Deborah; awake, awake, utter a song” (Judges 5:12), because her prophecy had left her.
רֵישׁ לָקִישׁ אָמַר: כׇּל אָדָם שֶׁכּוֹעֵס, אִם חָכָם הוּא — חׇכְמָתוֹ מִסְתַּלֶּקֶת מִמֶּנּוּ, אִם נָבִיא הוּא — נְבוּאָתוֹ מִסְתַּלֶּקֶת מִמֶּנּוּ. אִם חָכָם הוּא חׇכְמָתוֹ מִסְתַּלֶּקֶת מִמֶּנּוּ — מִמֹּשֶׁה, דִּכְתִיב: ״וַיִּקְצוֹף מֹשֶׁה עַל פְּקוּדֵי הֶחָיִל וְגוֹ׳״, וּכְתִיב: ״וַיֹּאמֶר אֶלְעָזָר הַכֹּהֵן אֶל אַנְשֵׁי הַצָּבָא הַבָּאִים לַמִּלְחָמָה זֹאת חֻקַּת הַתּוֹרָה אֲשֶׁר צִוָּה ה׳ אֶת מֹשֶׁה וְגוֹ׳״, מִכְּלָל דְּמֹשֶׁה אִיעֲלַם מִינֵּיהּ.
Similarly, Reish Lakish said: Any person who becomes angry, if he is a Torah scholar, his wisdom departs from him, and if he is a prophet, his prophecy departs from him. The Gemara explains: That if he is a Torah scholar his wisdom departs from him is learned from Moses, as it is written: “And Moses became angry with the officers of the host, the captains over thousands and the captains over hundreds, who came from the battle” (Numbers 31:14). And what was his punishment? As it is written afterward: “And Elazar the priest said to the men of war who went to the battle: This is the statute of the law, which the Lord commanded Moses” (Numbers 31:21), which proves by inference that this law had become hidden from Moses due to his anger.
אִם נָבִיא הוּא נְבוּאָתוֹ מִסְתַּלֶּקֶת מִמֶּנּוּ — מֵאֱלִישָׁע, דִּכְתִיב: ״לוּלֵי פְּנֵי יְהוֹשָׁפָט מֶלֶךְ יְהוּדָה אֲנִי נוֹשֵׂא אִם אַבִּיט אֵלֶיךָ וְאִם אֶרְאֶךָּ וְגוֹ׳״, וּכְתִיב: ״וְעַתָּה קְחוּ לִי מְנַגֵּן וְהָיָה כְּנַגֵּן הַמְנַגֵּן וַתְּהִי עָלָיו יַד ה׳ וְגוֹ׳״.
And that if he is a prophet, his prophecy departs from him, we learn from Elisha, as it is written that he became angry with the king of Israel and said to him: “Were it not that I have regard for the presence of Jehoshaphat the king of Judea, I would not look toward you, nor see you” (II Kings 3:14), and it is afterward written: “But now bring me a minstrel; and it came to pass when the minstrel played that the hand of the Lord came upon him” (II Kings 3:15). Because Elisha became angry with the king of Israel, his prophetic spirit departed from him and a minstrel was needed to rouse it anew.
אָמַר רַבִּי מָנִי בַּר פַּטִּישׁ: כׇּל שֶׁכּוֹעֵס, אֲפִילּוּ פּוֹסְקִין עָלָיו גְּדוּלָּה מִן הַשָּׁמַיִם — מוֹרִידִין אוֹתוֹ. מְנָלַן? מֵאֱלִיאָב, שֶׁנֶּאֱמַר: ״וַיִּחַר אַף אֱלִיאָב בְּדָוִד וַיֹּאמֶר לָמָּה [זֶּה] יָרַדְתָּ וְעַל מִי נָטַשְׁתָּ מְעַט הַצֹּאן הָהֵנָּה בַּמִּדְבָּר אֲנִי יָדַעְתִּי אֶת זְדֹנְךָ וְאֵת רוֹעַ לְבָבֶךָ כִּי לְמַעַן רְאוֹת הַמִּלְחָמָה יָרָדְתָּ״. וְכִי אֲזַל שְׁמוּאֵל לְמִמְשְׁחִינְהוּ, בְּכֻלְּהוּ כְּתִיב: ״לֹא בָּזֶה בָחַר ה׳״, וּבֶאֱלִיאָב כְּתִיב: ״וַיֹּאמֶר ה׳ אֶל שְׁמוּאֵל אַל תַּבֵּיט אֶל מַרְאֵהוּ וְאֶל גְּבֹהַּ קוֹמָתוֹ כִּי מְאַסְתִּיהוּ״, מִכְּלָל דַּהֲוָה רָחֵים לֵיהּ עַד הָאִידָּנָא.
Rabbi Mani bar Patish said: Whoever becomes angry, even if greatness has been apportioned to him from heaven, he is lowered from his greatness. From where do we derive this? From Eliab, David’s older brother, as it is stated: “And Eliab’s anger burned against David and he said: Why did you come down, and with whom have you left those few sheep in the wilderness? I know your insolence and the evil of your heart, for you have come down to see the battle” (I Samuel 17:28); we see that Eliab became angry. And when Samuel went to anoint him after God had told him that one of Yishai’s sons was to be the king, concerning all of the other brothers it is written: “The Lord has not chosen this one” (I Samuel 16:8), whereas with regard to Eliab it is written: “And the Lord said to Samuel: Look not at his appearance, nor at the height of his stature, for I have rejected him” (I Samuel 16:7). This proves by inference that until now He had loved him, and it was only at this point that Eliab was rejected. Had it not been for his anger, Eliab would have been fit for greatness; but owing to this shortcoming, God rejected him.
אַשְׁכְּחַן תָּמִיד וּפֶסַח דְּדָחוּ שַׁבָּת, דְּדָחוּ טוּמְאָה מְנָא לַן? אָמְרִי: כִּי הֵיכִי דְּיָלֵיף פֶּסַח מִתָּמִיד לְעִנְיַן שַׁבָּת, הָכִי נָמֵי יָלֵיף תָּמִיד מִפֶּסַח לְעִנְיַן טוּמְאָה.
The Gemara raises an additional question incidental to the previous discussion proving that the Paschal lamb overrides Shabbat: We have found proofs that the daily offering and the Paschal lamb override Shabbat. From where do we derive that they also override ritual impurity? For we have a tradition that if the entire community is ritually impure, they nonetheless offer the communal sacrifices and the Paschal lamb. They say: Just as the law governing the Paschal lamb is derived from the law governing the daily offering in regard to the overriding of Shabbat, so too the law concerning the daily offering is derived from the law concerning the Paschal lamb in regard to ritual impurity; just as the Paschal lamb overrides communal impurity, so does the daily offering.
וּפֶסַח גּוּפֵיהּ מְנָא לַן? אָמַר רַבִּי יוֹחָנָן: דְּאָמַר קְרָא ״אִישׁ אִישׁ כִּי יִהְיֶה טָמֵא לָנֶפֶשׁ״. אִישׁ נִדְחֶה לְפֶסַח שֵׁנִי, וְאֵין צִיבּוּר נִידְחִין לְפֶסַח שֵׁנִי, אֶלָּא עָבְדִי בְּטוּמְאָה.
The Gemara asks: And with regard to the Paschal lamb itself, from where do we derive that if most of the nation is ritually impure, the sacrifice is offered anyway? Rabbi Yoḥanan said: For the verse states: “Speak to the children of Israel, saying: Any man of you or your generations who shall be impure by reason of a corpse, or on a distant journey, he shall keep the Passover to the Lord. On the fourteenth day of the second month at evening they shall keep it, and eat it with matzot and bitter herbs” (Numbers 9:10–11). We can infer from here that a single individual or a group of individuals are deferred to the second Pesaḥ if they are ritually impure, but the entire community or the majority thereof is not deferred to the second Pesaḥ; rather, they observe the first Pesaḥ in a state of ritual impurity.
אֲמַר לֵיהּ רַבִּי שִׁמְעוֹן בֶּן לָקִישׁ לְרַבִּי יוֹחָנָן: אֵימָא, אִישׁ נִדְחֶה לְפֶסַח שֵׁנִי, צִיבּוּר לֵית לְהוּ תַּקַּנְתָּא לָא בְּפֶסַח רִאשׁוֹן וְלָא בְּפֶסַח שֵׁנִי!
Rabbi Shimon ben Lakish said to Rabbi Yoḥanan: This verse cannot serve as proof, for you can say that it is to be understood as follows: A single individual or a group of individuals is deferred to the second Pesaḥ, but the community has no remedy, neither on the first Pesaḥ nor on the second Pesaḥ.
אֶלָּא אָמַר רַבִּי שִׁמְעוֹן בֶּן לָקִישׁ, מֵהָכָא: ״וִישַׁלְּחוּ מִן הַמַּחֲנֶה כׇּל צָרוּעַ וְכׇל זָב וְכֹל טָמֵא לָנָפֶשׁ״, יֵאָמֵר טְמֵאֵי מֵתִים וְאַל יֵאָמֵר זָבִין וּמְצוֹרָעִין, וַאֲנִי אוֹמֵר: אִם טְמֵאֵי מֵתִים, מִשְׁתַּלְחִין, זָבִין וּמְצוֹרָעִין — לֹא כׇּל שֶׁכֵּן?
Rather, Rabbi Shimon ben Lakish rejected this proof and said that a different proof may be brought from here: “Command the children of Israel that they send out from the camp any leper and any zav and anyone impure by reason of a corpse” (Numbers 5:2). Let the verse say only that they are to send out those who are ritually impure due to a corpse, and not say anything about zavin and lepers, and I would say this law on my own through an a fortiori inference: If those ritually impure due to a corpse, whose impurity is not so severe as it is contracted from an external source, are sent out from the camp, with regard to zavin and lepers who are the source of their own impurity, all the more so is it not clear that they should be sent out? Thus, the verse contains unnecessary information.