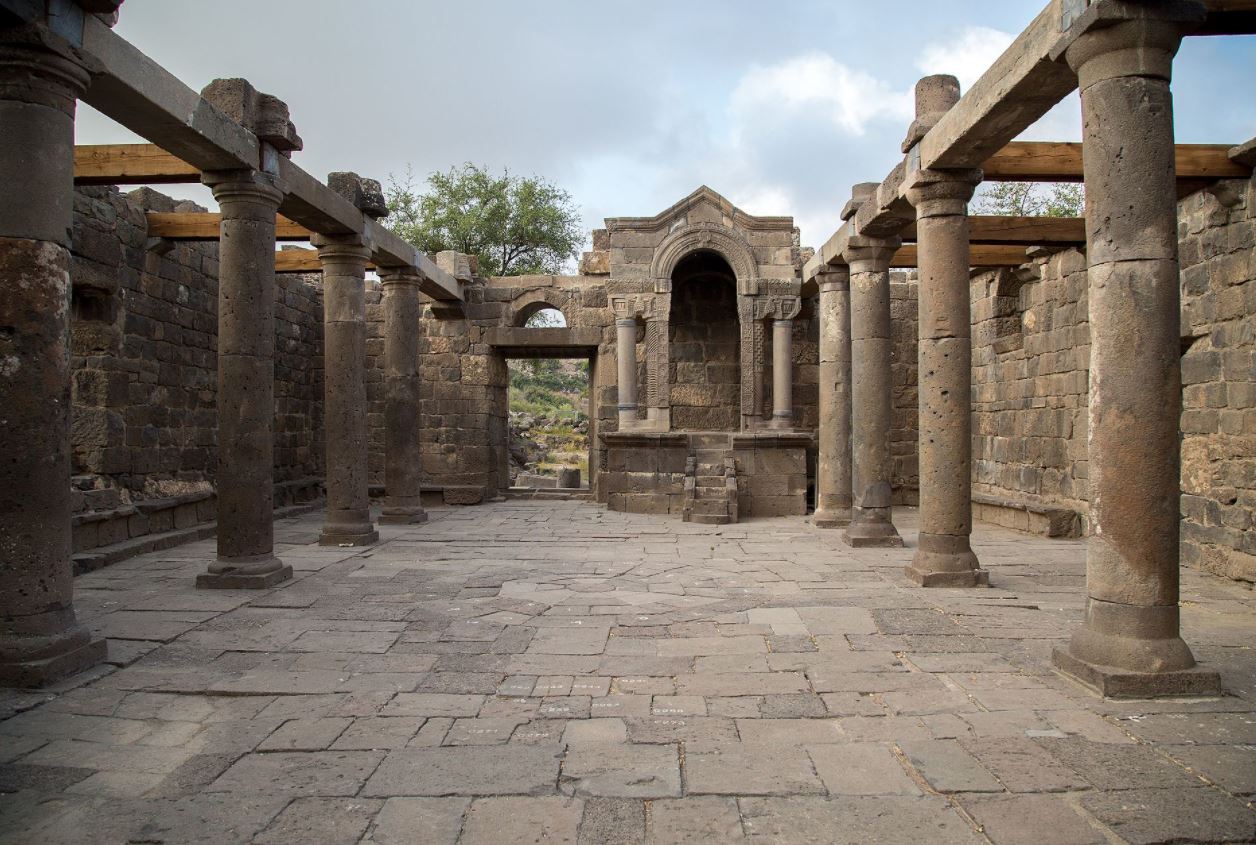
What are the different opinions regarding aliyot on Shabbat, Yom Tov and Yom Kippur? Regarding services on those days – on which days should the prayers start later and end earlier/start later and end later/start earlier and end earlier? Why? Does this have anything to do with how many aliyot there are on those days? The three aliyot on Mondays, Thursdays, etc., the five on Yom Tov and the seven on Shabbat – to what do they correspond? What about the six on Yom Kippur? Women and children can be among the seven who read from the Torah but the rabbis said that women should not due to “respect for the community.” How can this be understood? The person who reads from the prophets, the maftir, also reads a part of the Torah so as not to show disrespect for the Torah. Since the whole reason is just out of respect for the Torah, is this Aliya in addition to the seven or can it be considered part of the seven? The haftorah must be a minimum of twenty-one verses. What is the significance of that number? Are there exceptions to this rule? What prayers must be done with a quorum (minyan) of ten? From where do we learn the number ten? From where do we derive that each of these prayers needs a minyan?
Megillah 23
Share this shiur:
Megillah
Masechet Megilah is sponsored by Jordana and Kalman Schoor on behalf of their daughter Daria Esther who is completing Masechet Megilla in honor of her Bat Mitzva. Mazal tov!
Want to dedicate learning? Get started here:


Today’s daily daf tools:
Megillah
Masechet Megilah is sponsored by Jordana and Kalman Schoor on behalf of their daughter Daria Esther who is completing Masechet Megilla in honor of her Bat Mitzva. Mazal tov!
Today’s daily daf tools:
Delve Deeper
Broaden your understanding of the topics on this daf with classes and podcasts from top women Talmud scholars.
New to Talmud?
Check out our resources designed to help you navigate a page of Talmud – and study at the pace, level and style that fits you.
The Hadran Women’s Tapestry
Meet the diverse women learning Gemara at Hadran and hear their stories.
Megillah 23
וְרָבָא דִּמְצַלֵּי אַצְלוֹיֵי.
and Rava, who would bend their heads and not actually prostrate themselves on the ground.
בְּיוֹם טוֹב חֲמִשָּׁה, בְּיוֹם הַכִּפּוּרִים שִׁשָּׁה כּוּ׳. מַתְנִיתִין מַנִּי? לֹא רַבִּי יִשְׁמָעֵאל וְלָא רַבִּי עֲקִיבָא. דְּתַנְיָא: בְּיוֹם טוֹב חֲמִשָּׁה, וּבְיוֹם הַכִּפּוּרִים שִׁשָּׁה, וּבְשַׁבָּת שִׁבְעָה, אֵין פּוֹחֲתִין מֵהֶן וְאֵין מוֹסִיפִין עֲלֵיהֶן, דִּבְרֵי רַבִּי יִשְׁמָעֵאל. רַבִּי עֲקִיבָא אוֹמֵר: בְּיוֹם טוֹב חֲמִשָּׁה, וּבְיוֹם הַכִּפּוּרִים שִׁבְעָה, וּבְשַׁבָּת שִׁשָּׁה, אֵין פּוֹחֲתִין מֵהֶן אֲבָל מוֹסִיפִין עֲלֵיהֶן.
We learned in the mishna: On a Festival, five people read; on Yom Kippur, six people read; and on Shabbat, seven people read. One may not decrease the number of readers, but one may add to them. The Gemara asks: Who is the tanna of the mishna? It is not Rabbi Yishmael and not Rabbi Akiva, as it is taught in a baraita: On a Festival, five people read from the Torah; and on Yom Kippur, six people read; and on Shabbat, seven people read. One may not decrease or add to the required number of readers. This is the statement of Rabbi Yishmael. Rabbi Akiva disagrees and says: On a Festival, five people read from the Torah; and on Yom Kippur, seven people read; and on Shabbat, six people read. One may not decrease these numbers, but one may add to them.
מַנִּי? אִי רַבִּי יִשְׁמָעֵאל — קַשְׁיָא תּוֹסֶפֶת! אִי רַבִּי עֲקִיבָא — קַשְׁיָא שִׁשָּׁה וְשִׁבְעָה!
Who is the tanna of the mishna? If you say it is Rabbi Yishmael, it is difficult due to the ruling with regard to adding, as the mishna states that one may add additional readers but Rabbi Yishmael holds that one may not do so. If you say it is Rabbi Akiva, it is difficult due to the ruling concerning the days on which there are six and seven readers.
אָמַר רָבָא: תְּנָא דְּבֵי רַבִּי יִשְׁמָעֵאל הִיא. דְּתָנָא דְּבֵי רַבִּי יִשְׁמָעֵאל: בְּיוֹם טוֹב חֲמִשָּׁה, בְּיוֹם הַכִּפּוּרִים שִׁשָּׁה, בְּשַׁבָּת שִׁבְעָה, אֵין פּוֹחֲתִין מֵהֶן אֲבָל מוֹסִיפִין עֲלֵיהֶן, דִּבְרֵי רַבִּי יִשְׁמָעֵאל.
Rava said: It is the tanna of the school of Rabbi Yishmael, as it was taught in the school of Rabbi Yishmael: On a Festival, five people read from the Torah; on Yom Kippur, six people read; on Shabbat, seven people read. One may not decrease these numbers but one may add to them. This is the statement of Rabbi Yishmael.
קַשְׁיָא דְּרַבִּי יִשְׁמָעֵאל אַדְּרַבִּי יִשְׁמָעֵאל! תְּרֵי תַּנָּאֵי אַלִּיבָּא דְּרַבִּי יִשְׁמָעֵאל.
The Gemara comments: If so, there is a contradiction between the opinion of Rabbi Yishmael, as expressed in the mishna, and the opinion of Rabbi Yishmael himself, as recorded in the baraita. The Gemara responds: Two tanna’im, students of Rabbi Yishmael, expressed different opinions in accordance with the opinion of Rabbi Yishmael.
מַאן תְּנָא לְהָא דְּתַנְיָא: בְּיוֹם טוֹב מְאַחֲרִין לָבוֹא, וּמִמֻּהְרִין לָצֵאת. בְּיוֹם הַכִּפּוּרִים מִמֻּהְרִין לָבוֹא, וּמְאַחֲרִין לָצֵאת. וּבְשַׁבָּת מִמֻּהְרִין לָבוֹא, וּמִמֻּהְרִין לָצֵאת. לֵימָא רַבִּי עֲקִיבָא, דְּאִית לֵיהּ גַּבְרָא יַתִּירָא? אֲפִילּוּ תֵּימָא רַבִּי יִשְׁמָעֵאל — דִּנְפִישׁ סִידּוּרָא דְּיוֹמָא.
The Gemara asks: Who is the tanna who taught that which is taught in a baraita: On a Festival, one is slow to arrive at the synagogue because one is busy preparing for the festive meal, and one is quick to leave in order to eat; on Yom Kippur, one is quick to arrive at the synagogue and slow to leave; and on Shabbat, one is quick to arrive, as the meal has been prepared before Shabbat, and quick to leave in order to eat the Shabbat meal? Let us say it is Rabbi Akiva, who holds that an additional man reads from the Torah on Yom Kippur, which prolongs the service on that day. The Gemara rejects this suggestion: Even if you say it is Rabbi Yishmael, one leaves the synagogue late because the order of the day, i.e., the prayer service, is very long, as it includes many supplications and confessions.
הָנֵי שְׁלֹשָׁה חֲמִשָּׁה וְשִׁבְעָה כְּנֶגֶד מִי? פְּלִיגִי בַּהּ רַבִּי יִצְחָק בַּר נַחְמָנִי וְחַד דְּעַמְיָה, וּמַנּוּ — רַבִּי שִׁמְעוֹן בֶּן פַּזִּי. וְאָמְרִי לַהּ: רַבִּי שִׁמְעוֹן בֶּן פַּזִּי וְחַד דְּעַמֵּיהּ, וּמַנּוּ — רַבִּי יִצְחָק בַּר נַחְמָנִי, וְאָמְרִי לַהּ רַבִּי שְׁמוּאֵל בַּר נַחְמָנִי. חַד אָמַר: כְּנֶגֶד בִּרְכַּת כֹּהֲנִים, וְחַד אָמַר: כְּנֶגֶד שְׁלֹשָׁה שׁוֹמְרֵי הַסַּף, חֲמִשָּׁה מֵרוֹאֵי פְּנֵי הַמֶּלֶךְ, שִׁבְעָה רוֹאַי פְּנֵי הַמֶּלֶךְ.
A question is raised with regard to the number of readers on different days. Corresponding to what were these three, five, and seven, readers instituted? Rabbi Yitzḥak bar Naḥmani and one other Sage who was with him disagree about this. And who was that other scholar? Rabbi Shimon ben Pazi. And some say that this was a matter of dispute between Rabbi Shimon ben Pazi and one other scholar who was with him. And who was that other scholar? Rabbi Yitzḥak bar Naḥmani, and some say it was Rabbi Shmuel bar Naḥmani. One said: These numbers correspond to the number of Hebrew words in the three verses of the Priestly Benediction. And one said: These numbers correspond to the three guards of the door (II Kings 25:18), five of the officers who saw the king’s face (II Kings 25:19), and the seven officers who saw the king’s face (Esther 1:14).
תָּנֵי רַב יוֹסֵף: שְׁלֹשָׁה חֲמִשָּׁה וְשִׁבְעָה — שְׁלֹשָׁה שׁוֹמְרֵי הַסַּף, חֲמִשָּׁה מֵרוֹאֵי פְּנֵי הַמֶּלֶךְ, שִׁבְעָה רוֹאִי פְּנֵי הַמֶּלֶךְ. אָמַר לֵיהּ אַבָּיֵי: עַד הָאִידָּנָא מַאי טַעְמָא לָא פָּרִישׁ לַן מָר? אֲמַר לֵיהּ: לָא הֲוָה יָדַעְנָא דִּצְרִיכִיתוּ לֵיהּ, וּמִי בְּעֵיתוּ מִינַּאי מִילְּתָא וְלָא אֲמַרִי לְכוּ?!
Similarly, Rav Yosef taught a baraita: The three, five, and seven people who read from the Torah correspond to the three guards of the door, five of the officers who saw the king’s face, and the seven officers who saw the king’s face. When Rav Yosef taught this, Abaye said to him: What is the reason that until now the Master did not explain the matter to us in this way? Rav Yosef said to him: I did not know that you needed this information, as I thought that you were already familiar with the baraita. Have you ever asked me something and I did not tell you?
אֲמַר לֵיהּ יַעֲקֹב מִינָאָה לְרַב יְהוּדָה: הָנֵי שִׁשָּׁה דְּיוֹם הַכִּפּוּרִים כְּנֶגֶד מִי? אֲמַר לֵיהּ: כְּנֶגֶד שִׁשָּׁה שֶׁעָמְדוּ מִימִינוֹ שֶׁל עֶזְרָא וְשִׁשָּׁה מִשְּׂמֹאלוֹ, שֶׁנֶּאֱמַר: ״וַיַּעֲמוֹד עֶזְרָא הַסּוֹפֵר עַל מִגְדַּל עֵץ אֲשֶׁר עָשׂוּ לַדָּבָר וַיַּעֲמוֹד אֶצְלוֹ מַתִּתְיָה וְשֶׁמַע וַעֲנָיָה וְאוּרִיָּה וְחִלְקִיָּה וּמַעֲשֵׂיָה עַל יְמִינוֹ וּמִשְּׂמֹאלוֹ פְּדָיָה וּמִישָׁאֵל וּמַלְכִּיָּה וְחָשׁוּם וְחַשְׁבַּדָּנָה זְכַרְיָה מְשֻׁלָּם״.
Ya’akov of Mina said to Rav Yehuda: Corresponding to whom were these six readers on Yom Kippur instituted? Rav Yehuda said to him: The number six corresponds to the six people who stood to Ezra’s right and the six people who stood to his left, as it is stated: “And Ezra the Scribe stood upon a platform of wood, which they had made for the purpose, and beside him stood Mattithiah, and Shema, and Anaiah, and Uriah, and Hilkiah, and Maaseiah, on his right hand, and on his left hand, Pedaiah, and Mishael, and Malchiah, and Hashum, and Hashbadanah, Zechariah, Meshullam” (Nehemiah 8:4).
הָנֵי שִׁבְעָה הָווּ! הַיְינוּ ״זְכַרְיָה״ הַיְינוּ ״מְשֻׁלָּם״, וְאַמַּאי קְרָאוֹ ״מְשֻׁלָּם״? דְּמִישְׁלָם בְּעוֹבָדֵיהּ.
The Gemara challenges this answer: Those that stood to his left were seven and not six. The Gemara responds: Zechariah is the same as Meshullam, that is to say, they are not two separate people, but rather one person with two names. And why was he called Meshullam? Because he was perfect [mishlam] in his actions.
תָּנוּ רַבָּנַן: הַכֹּל עוֹלִין לַמִּנְיָן שִׁבְעָה, וַאֲפִילּוּ קָטָן וַאֲפִילּוּ אִשָּׁה. אֲבָל אָמְרוּ חֲכָמִים: אִשָּׁה לֹא תִּקְרָא בְּתוֹרָה, מִפְּנֵי כְּבוֹד צִבּוּר.
§ The Sages taught in a Tosefta (Megilla 3:11): All people count toward the quorum of seven readers, even a minor and even a woman. However, the Sages said that a woman should not read the Torah, out of respect for the congregation.
אִיבַּעְיָא לְהוּ: מַפְטִיר, מַהוּ שֶׁיַּעֲלֶה לַמִּנְיָן שִׁבְעָה? רַב הוּנָא וְרַבִּי יִרְמְיָה בַּר אַבָּא, חַד אָמַר: עוֹלֶה, וְחַד אָמַר: אֵינוֹ עוֹלֶה. מַאן דְּאָמַר עוֹלָה — דְּהָא קָרֵי,
A dilemma was raised before the Sages: With regard to the reader who concludes [maftir] the Torah reading and reads from the Prophets [haftara], what is the halakha; does he count toward the quorum of seven readers? Rav Huna and Rabbi Yirmeya bar Abba disagreed about this matter. One said: He counts, and one said: He does not count. The one who said that he counts toward the seven readers holds that opinion because he reads from the Torah.
וּמַאן דְּאָמַר אֵינוֹ עוֹלֶה — כִּדְעוּלָּא. דְּאָמַר עוּלָּא: מִפְּנֵי מָה הַמַּפְטִיר בְּנָבִיא צָרִיךְ שִׁיקְרָא בְּתוֹרָה תְּחִלָּה — מִפְּנֵי כְּבוֹד תּוֹרָה, וְכֵיוָן דְּמִשּׁוּם כְּבוֹד תּוֹרָה הוּא — לְמִנְיָנָא לָא סָלֵיק.
And the one who said that he does not count holds in accordance with the opinion of Ulla, as Ulla said: For what reason must the one who concludes with a reading from the Prophets read from the Torah first? It is due to respect for the Torah, so that those present should not conclude that he was called up only to read from the Prophets because the honor due the Torah and the honor due the Prophets are equal. And since he reads only out of respect for the Torah, he is not included in the quorum of seven readers.
מֵיתִיבִי: הַמַּפְטִיר בְּנָבִיא לֹא יִפְחוֹת מֵעֶשְׂרִים וְאֶחָד פְּסוּקִין, כְּנֶגֶד שִׁבְעָה שֶׁקְּרָאוֹ בְּתוֹרָה. וְאִם אִיתָא, עֶשְׂרִים וְאַרְבָּעָה הָוְיִין! כֵּיוָן דְּמִשּׁוּם כְּבוֹד תּוֹרָה הוּא —
The Gemara raises an objection based upon the following baraita: The one who concludes with a reading from the Prophets may not read fewer than twenty-one verses, corresponding to the seven who read from the Torah. Each one who reads from the Torah must read at least three verses, for a total of at least twenty-one verses. And if it is so, that the one who reads the haftara does not count toward the quorum of seven readers, and he is an eighth reader, the minimum number of verses that must be read from the Torah is twenty-four and not twenty-one. The Gemara answers: Since the one who reads the haftara reads from the Torah first only due to respect for the Torah,
כְּנֶגְדּוֹ נָמֵי לָא בָּעֵי.
it is not necessary to also add corresponding verses in the haftara.
מַתְקֵיף לַהּ רָבָא: וַהֲרֵי ״עוֹלוֹתֵיכֶם סְפוֹ״, דְּלָא הָוְיִין עֶשְׂרִין וְחַד, וְקָרֵינַן! שָׁאנֵי הָתָם, דִּסְלֵיק עִנְיָינָא.
Rava strongly objects to this baraita: But there is the haftara that begins with the words: “Add your burnt offerings” (Jeremiah 7:21–28), which does not have twenty-one verses, and nevertheless we read it. The Gemara answers: There it is different, as the topic is completed in fewer than twenty-one verses, and it is not necessary to begin another topic merely to complete the number of verses.
וְהֵיכָא דְּלָא סָלֵיק עִנְיָינָא לָא? וְהָאָמַר רַב שְׁמוּאֵל בַּר אַבָּא: זִמְנִין סַגִּיאִין הֲוָה קָאֵימְנָא קַמֵּיהּ דְּרַבִּי יוֹחָנָן, וְכִי הֲוָה קָרֵינַן עֲשָׂרָה פְּסוּקֵי, אֲמַר לַן: אַפְּסִיקוֹ! מָקוֹם שֶׁיֵּשׁ תּוּרְגְּמָן שָׁאנֵי. דְּתָנֵי רַב תַּחְלִיפָא בַּר שְׁמוּאֵל: לֹא שָׁנוּ אֶלָּא בִּמְקוֹם שֶׁאֵין תּוּרְגְּמָן, אֲבָל מָקוֹם שֶׁיֵּשׁ תּוּרְגְּמָן — פּוֹסֵק.
The Gemara asks: But is it true that where the topic is not completed, we do not read fewer than twenty-one verses? Didn’t Rav Shmuel bar Abba say: Many times I stood before Rabbi Yoḥanan as a translator, and when we had read ten verses he would say to us: Stop. This indicates that a haftara need not be twenty-one verses. The Gemara answers: In a place where there is a translator, who translates each verse into Aramaic and adds additional explanation, it is different. In that case, it is not necessary for the haftara to consist of twenty-one verses, so as not to overburden the congregation, as Rav Taḥalifa bar Shmuel taught: They taught that twenty-one verses must be read from the haftara only in a place where there is no translator; but in a place where there is a translator, one may stop even before that.
מַתְנִי׳ אֵין פּוֹרְסִין עַל שְׁמַע, וְאֵין עוֹבְרִין לִפְנֵי הַתֵּיבָה, וְאֵין נוֹשְׂאִין אֶת כַּפֵּיהֶם, וְאֵין קוֹרִין בְּתוֹרָה, וְאֵין מַפְטִירִין בַּנָּבִיא,
MISHNA: One does not recite the introductory prayers and blessing [poresin] before Shema; nor does one pass before the ark to repeat the Amida prayer; nor do the priests lift their hands to recite the Priestly Benediction; nor is the Torah read in public; nor does one conclude with a reading from the Prophets [haftara] in the presence of fewer than ten men.
וְאֵין עוֹשִׂין מַעֲמָד וּמוֹשָׁב, וְאֵין אוֹמְרִים בִּרְכַּת אֲבֵלִים וְתַנְחוּמֵי אֲבֵלִים, וּבִרְכַּת חֲתָנִים, וְאֵין מְזַמְּנִין בְּשֵׁם — פָּחוֹת מֵעֲשָׂרָה. וּבְקַרְקָעוֹת — תִּשְׁעָה וְכֹהֵן, וְאָדָם כַּיּוֹצֵא בָּהֶן.
And one does not observe the practice of standing up and sitting down for the delivery of eulogies at a funeral service; nor does one recite the mourners’ blessing or comfort mourners in two lines after the funeral; or recite the bridegrooms’ blessing; and one does not invite others to recite Grace after Meals, i.e., conduct a zimmun, with the name of God, with fewer than ten men present. If one consecrated land and now wishes to redeem it, the land must be assessed by nine men and one priest, for a total of ten. And similarly, assessing the value of a person who has pledged his own value to the Temple must be undertaken by ten people, one of whom must be a priest.
גְּמָ׳ מְנָא הָנֵי מִילֵּי? אָמַר רַבִּי חִיָּיא בַּר אַבָּא אָמַר רַבִּי יוֹחָנָן, דְּאָמַר קְרָא: ״וְנִקְדַּשְׁתִּי בְּתוֹךְ בְּנֵי יִשְׂרָאֵל״, כׇּל דָּבָר שֶׁבִּקְדוּשָּׁה לֹא יְהֵא פָּחוֹת מֵעֲשָׂרָה.
GEMARA: The Gemara asks: From where are these matters, i.e., that ten people are needed in each of these cases, derived? Rabbi Ḥiyya bar Abba said that Rabbi Yoḥanan said: It is as the verse states: “And I shall be hallowed among the children of Israel” (Leviticus 22:32), which indicates that any expression of sanctity may not be recited in a quorum of fewer than ten men.
מַאי מַשְׁמַע? דְּתָנֵי רַבִּי חִיָּיא: אָתְיָא ״תּוֹךְ״ ״תּוֹךְ״, כְּתִיב הָכָא: ״וְנִקְדַּשְׁתִּי בְּתוֹךְ בְּנֵי יִשְׂרָאֵל״, וּכְתִיב הָתָם: ״הִבָּדְלוּ מִתּוֹךְ הָעֵדָה״,
The Gemara asks: From where in the verse may this be inferred? The Gemara responds that it must be understood as Rabbi Ḥiyya taught: It is inferred by means of a verbal analogy [gezera shava] between the words “among,” “among.” Here, it is written: “And I shall be hallowed among the children of Israel,” and there, with regard to Korah’s congregation, it is written “Separate yourselves from among this congregation” (Numbers 16:21). Just as with regard to Korah the reference is to ten men, so too, the name of God is to be hallowed in a quorum of ten men.
וְאָתְיָא ״עֵדָה״ ״עֵדָה״, דִּכְתִיב הָתָם: ״עַד מָתַי לָעֵדָה הָרָעָה הַזֹּאת״ — מָה לְהַלָּן עֲשָׂרָה, אַף כָּאן עֲשָׂרָה.
The connotation of ten associated with the word “among” in the portion of Korah is, in turn, inferred by means of another verbal analogy between the word “congregation” written there and the word “congregation” written in reference to the ten spies who slandered Eretz Yisrael, as it is written there: “How long shall I bear with this evil congregation?” (Numbers 14:27). Consequently, just as there, in the case of the spies, it was a congregation of ten people, as there were twelve spies altogether, and Joshua and Caleb were not included in the evil congregation, so too, here, in the case of Korah, the reference is to a congregation of ten people. The first several items mentioned in the mishna are expressions of sanctity, and they consequently require a quorum of ten.
וְאֵין עוֹשִׂין מַעֲמָד וּמוֹשָׁב פָּחוֹת מֵעֲשָׂרָה. כֵּיוָן דְּבָעֵי לְמֵימַר: ״עִמְדוּ יְקָרִים עֲמוֹדוּ, שְׁבוּ יְקָרִים שֵׁבוּ״ — בְּצִיר מֵעֲשָׂרָה לָאו אוֹרַח אַרְעָא.
§ We learned in the mishna: And one does not observe the practice of standing up and sitting down for the delivery of eulogies at a funeral service with fewer than ten men present. As this is not an expression of sanctity, it is therefore necessary to explain why a quorum is required. The Gemara explains: Since the leader of the funeral procession is required to say: Stand, dear friends, stand; sit down, dear friends, sit down, when there are fewer than ten it is not proper conduct to speak in such a dignified style.
וְאֵין אוֹמְרִים בִּרְכַּת אֲבֵלִים וּבִרְכַּת חֲתָנִים (וְכוּ׳). מַאי בִּרְכַּת אֲבֵלִים? בִּרְכַּת רְחָבָה. דְּאָמַר רַבִּי יִצְחָק אָמַר רַבִּי יוֹחָנָן: בִּרְכַּת אֲבֵלִים בַּעֲשָׂרָה, וְאֵין אֲבֵלִים מִן הַמִּנְיָן. בִּרְכַּת חֲתָנִים בַּעֲשָׂרָה, וַחֲתָנִים מִן הַמִּנְיָן.
We also learned in the mishna that one does not recite the mourners’ blessing and the bridegrooms’ blessing with fewer than ten men present. The Gemara asks: What is the mourners’ blessing? The blessing recited in the square next to the cemetery. Following the burial, those who participated in the funeral would assemble in the square and bless the mourners that God should comfort them, as Rabbi Yitzḥak said that Rabbi Yoḥanan said: The mourners’ blessing is recited only with ten men present, and mourners themselves are not included in the count. The bridegrooms’ blessing is also recited only with ten men present, and bridegrooms themselves are included in the count. Consequently, only nine other men are needed.
וְאֵין מְזַמְּנִין עַל הַמָּזוֹן בַּשֵּׁם פָּחוֹת מֵעֲשָׂרָה (וְכוּ׳). כֵּיוָן דְּבָעֵי לְמֵימַר ״נְבָרֵךְ לֵאלֹהֵינוּ״ — בְּצִיר מֵעֲשָׂרָה לָאו אוֹרַח אַרְעָא.
We learned further in the mishna: And one does not invite others to recite Grace after Meals, i.e., conduct a zimmun, in order to thank God for one’s nourishment, with the name of God, with fewer than ten men present. Since one is required to say: Let us bless our Lord, in the presence of fewer than ten it is not proper conduct to mention the name of God.
וְהַקַּרְקָעוֹת תִּשְׁעָה וְכֹהֵן, וְאָדָם כַּיּוֹצֵא בָּהֶן (וְכוּ׳). מְנָא הָנֵי מִילֵּי?
§ If one consecrated land and now wishes to redeem it, the land must be assessed by nine Israelites and one priest, for a total of ten. And similarly, assessing the value of a person who has pledged his own value to the Temple must be undertaken by ten people, one of whom must be a priest. The Gemara asks: From where are these matters, that consecrated land must be assessed by ten people, one of whom is a priest, derived?
אָמַר שְׁמוּאֵל: עֲשָׂרָה כֹּהֲנִים כְּתוּבִים בַּפָּרָשָׁה. חַד לְגוּפֵיהּ, (וְחַד לְמַעוֹטֵי,) וְאִידַּךְ הָוֵי מִיעוּט אַחַר מִיעוּט, וְאֵין מִיעוּט אַחַר מִיעוּט אֶלָּא לְרַבּוֹת. תִּשְׁעָה יִשְׂרְאֵלִים וְחַד כֹּהֵן.
Shmuel said: The word priest is written ten times in the Torah portion that addresses the redemption of consecrated property, indicating that ten people are required to assess the value of such property (Leviticus, chapter 27). One instance of the word is needed for itself, to indicate that a priest must participate in the assessment. And one instance is needed to exclude all non-priests from fulfilling that role. And all the other instances of the word are restrictions following other restrictions, and there is a general hermeneutical principle that one restriction after another serves only to amplify. Therefore, each additional time the word priest is repeated, it extends the criteria applied to appraisers, so as to allow non-priests to participate. Consequently, the assessment may be carried out by nine ordinary Israelites and one priest.
וְאֵימָא: חֲמִשָּׁה כֹּהֲנִים וַחֲמִשָּׁה יִשְׂרְאֵלִים! קַשְׁיָא.
The Gemara asks: And on the basis of this principle, say that the first usage of the term is restrictive and requires a priest for the assessment; the second usage amplifies and allows for a non-priest; the third usage again requires a priest; the fourth usage allows for a non-priest; and so on. Consequently, the assessment must be carried out by five priests and five ordinary Israelites. The Gemara concludes: Indeed, it is difficult, as the derivation has not been sufficiently explained.
וְאָדָם כַּיּוֹצֵא בָּהֶן. אָדָם מִי קָדוֹשׁ?
We learned in the mishna: And similarly, assessing the value of a person who has pledged his own value to the Temple must be undertaken by ten people, one of whom must be a priest. The Gemara asks: Can a person become consecrated and thereby require redemption?
אָמַר רַבִּי אֲבָהוּ: בְּאוֹמֵר ״דְּמֵי עָלַי״. דְּתַנְיָא: הָאוֹמֵר ״דְּמֵי עָלַי״ — שָׁמִין אוֹתוֹ כְּעֶבֶד. וְעֶבֶד אִיתַּקַּשׁ לְקַרְקָעוֹת, דִּכְתִיב: ״וְהִתְנַחַלְתֶּם אוֹתָם לִבְנֵיכֶם אַחֲרֵיכֶם לָרֶשֶׁת אֲחוּזָּה״.
Rabbi Abbahu said: The mishna is referring to one who says: My assessment is incumbent upon me, and thereby pledges to donate a sum of money equivalent to his own monetary value to the Temple treasury, as it is taught in a baraita: With regard to one who says: My assessment is incumbent upon me, the court assesses him as though he were a slave in order to determine the amount he is obligated to donate to the Temple treasury. And a slave is compared to land, as it is written with regard to slaves: “And you shall take them as an inheritance for your children after you, to inherit them for a possession” (Leviticus 25:46). Consequently, the same criteria that apply to assessing consecrated land apply to assessing the monetary value of an individual.
מַתְנִי׳ הַקּוֹרֵא בְּתוֹרָה — לֹא יִפְחוֹת מִשְּׁלֹשָׁה פְּסוּקִים, וְלֹא יִקְרָא לִמְתוּרְגְּמָן יוֹתֵר מִפָּסוּק אֶחָד.
MISHNA: One who reads from the Torah in the synagogue should not read fewer than three verses. And when it is being translated, he should not read to the translator more than one verse at a time, so that the translator will not become confused.