Shabbat 103
הַקּוֹדֵחַ כׇּל שֶׁהוּא — חַיָּיב. בִּשְׁלָמָא לְרַב — מֶיחְזֵי כְּמַאן דְּחַר חוֹרְתָא לְבִנְיָינָא, אֶלָּא לִשְׁמוּאֵל — לָאו גְּמַר מְלָאכָה הוּא! הָכָא בְּמַאי עָסְקִינַן — דְּבַזְעֵיהּ בְּרַמְצָא דְפַרְזְלָא וְשַׁבְקֵיהּ בְּגַוֵּויהּ, דְּהַיְינוּ גְּמַר מְלָאכָה.
One who drills a hole of any size is liable. Granted, according to Rav, who said that one who makes a hole is liable due to the prohibited labor of building, here too, he should be liable because he appears as one who is making a hole for the purpose of building. However, according to Shmuel, drilling a hole is not a completion of the labor. The labor will be complete only when a stake or pin is inserted into the hole. Until he does so, he cannot be liable for completing the labor. The Gemara answers: With what we are dealing here? With a case where one drilled a hole with an iron nail and left it inside the surface in which he drilled the hole. That is considered a completion of labor because there is no intention to remove the nail from its hole.
זֶה הַכְּלָל. ״זֶה הַכְּלָל״ לְאֵתוּיֵי מַאי? לְאֵתוּיֵי דְּחַק קְפִיזָא בְּקַבָּא.
We learned in the mishna that this is the principle: Anyone who performs a prohibited labor and his labor endures on Shabbat is liable. The Gemara asks: What does the phrase: This is the principle, come to include? The Gemara explains: It comes to include a case where one carved out a vessel with a capacity of half a kav [kefiza] into a piece of wood in which it was possible to chisel a vessel with a capacity of a whole kav. Since this labor endures on Shabbat and it can be used, it is considered a complete labor and he is liable.
רַבָּן שִׁמְעוֹן בֶּן גַּמְלִיאֵל אוֹמֵר: הַמַּכֶּה בְּקוּרְנָס עַל הַסַּדָּן כּוּ׳. מַאי קָעָבֵיד? רַבָּה וְרַב יוֹסֵף דְּאָמְרִי תַּרְוַיְיהוּ: מִפְּנֵי שֶׁמְאַמֵּן אֶת יָדוֹ. קָשׁוּ בָּהּ בְּנֵי רַחֲבָה: אֶלָּא מֵעַתָּה, חֲזָא אוּמָּנוּתָא בְּשַׁבְּתָא וּגְמַר, הָכִי נָמֵי דְּמִיחַיַּיב? אֶלָּא אַבָּיֵי וְרָבָא דְּאָמְרִי תַּרְוַיְיהוּ: שֶׁכֵּן מְרַדְּדֵי טַסֵּי מִשְׁכָּן עוֹשִׂין כֵּן. תַּנְיָא נָמֵי הָכִי, רַבָּן שִׁמְעוֹן בֶּן גַּמְלִיאֵל אוֹמֵר: אַף הַמַּכֶּה בְּקוּרְנָס עַל הַסַּדָּן בִּשְׁעַת מְלָאכָה — חַיָּיב, שֶׁכֵּן מְרַדְּדֵי טַסֵּי מִשְׁכָּן עוֹשִׂין כֵּן.
We also learned in the mishna that Rabban Shimon ben Gamliel says: Even one who strikes an anvil with a sledgehammer is liable. The Gemara wonders: What has he done by striking the anvil that would render him liable? It was Rabba and Rav Yosef who both said in explanation: He is liable because he trains his hand for his work by striking the anvil. The sons of a man named Raḥava found this answer difficult: If so, one who observed a craft being performed on Shabbat and learned to perform that craft through observation, would he also be liable? Only one who performs an actual labor on Shabbat is liable. Rather, it was Abaye and Rava who both said in explanation: He is liable, as those who flatten plates of metal for the Tabernacle do so. They would strike the anvil with the sledgehammer in order to straighten the sledgehammer’s handle, which became crooked. That was also taught in a baraita. Rabban Shimon ben Gamliel says: Even one who strikes an anvil with a sledgehammer during his labor is liable, as those who flatten plates of metal for the Tabernacle do so.
מַתְנִי׳ הַחוֹרֵשׁ כׇּל שֶׁהוּא, הַמְנַכֵּשׁ וְהַמְקַרְסֵם וְהַמְזָרֵד כׇּל שֶׁהוּא — חַיָּיב. הַמְלַקֵּט עֵצִים, אִם לְתַקֵּן — כׇּל שֶׁהֵן, אִם לְהֶיסֵּק — כְּדֵי לְבַשֵּׁל בֵּיצָה קַלָּה. הַמְלַקֵּט עֲשָׂבִים, אִם לְתַקֵּן — כׇּל שֶׁהוּא, אִם לִבְהֵמָה — כִּמְלֹא פִי הַגְּדִי.
MISHNA: One who plows is liable for plowing any amount of land on Shabbat. One who weeds and removes grass on Shabbat, and one who removes dry branches and who prunes any amount is liable. With regard to one who gathers wood, if he did so to enhance the tree or the land, he is liable for any amount; if he did so for fuel, he is liable for collecting a measure equivalent to that which is used to cook an easily cooked egg. With regard to one who gathers grass, if he did so to enhance the plants or the land, he is liable for any amount; if he did so to feed an animal, he is liable for collecting a measure equivalent to a goat’s mouthful.
גְּמָ׳ לְמַאי חֲזֵי? חֲזֵי לְבִיזְרָא דְקַרָא. דִּכְווֹתַהּ גַּבֵּי מִשְׁכָּן, שֶׁכֵּן רָאוּי לְקֶלַח אֶחָד שֶׁל סַמָּנִין.
GEMARA: The Gemara asks: For what use is plowing any amount of land suited? The Gemara answers: It is suited for a single pumpkin seed. The corresponding situation in the Tabernacle was as it is suitable for planting a single stalk of herbs to make dyes.
הַמְנַכֵּשׁ וְהַמְקַרְסֵם וְהַמְזָרֵד. תָּנוּ רַבָּנַן: הַתּוֹלֵשׁ עוּלְשִׁין וְהַמְזָרֵד זְרָדִים, אִם לַאֲכִילָה — כִּגְרוֹגֶרֶת. אִם לִבְהֵמָה — כִּמְלֹא פִי הַגְּדִי. אִם לְהֶיסֵּק — כְּדֵי לְבַשֵּׁל בֵּיצָה קַלָּה. אִם לְיַיפּוֹת אֶת הַקַּרְקַע — כׇּל שֶׁהֵן.
We also learned in the mishna: One who weeds, and one who removes dry branches, and who prunes any amount is liable. The Sages taught that in a baraita: With regard to one who severs endives that grow like weeds, or who prunes reeds [zeradim]; if he did so for human consumption, he is liable in the measure of a fig-bulk; if he did so for animal consumption, he is liable in a measure equivalent to a goat’s mouthful. If he did so for fuel, he is liable for severing a measure equivalent to that which is used to cook an easily cooked egg. If he did so to enhance the land, he is liable for any amount.
אַטּוּ כּוּלְּהוּ לָא לְיַפּוֹת אֶת הַקַּרְקַע נִינְהוּ? רַבָּה וְרַב יוֹסֵף דְּאָמְרִי תַּרְוַיְיהוּ: בַּאֲגַם שָׁנוּ. אַבָּיֵי אָמַר: אֲפִילּוּ תֵּימָא בְּשָׂדֶה דְּלָאו אֲגַם, וּכְגוֹן דְּלָא קָמִיכַּוֵּין. וְהָא אַבָּיֵי וְרָבָא דְּאָמְרִי תַּרְוַיְיהוּ: מוֹדֶה רַבִּי שִׁמְעוֹן, בִּ״פְסִיק רֵישֵׁיהּ וְלָא יְמוּת״! לָא צְרִיכָא, דְּקָעָבֵיד בְּאַרְעָא דְחַבְרֵיהּ.
The Gemara asks: Aren’t all these done to enhance the land? Each stalk that a person uproots enhances the land. It was Rabba and Rav Yosef who both said in explanation: They taught this baraita with regard to swampland, where grass is not uprooted to enhance the land. Abaye said: Even if you say that the baraita is referring to a field that is not a swampland, it can be referring to a case where one did not intend to enhance the land. The Gemara asks: However, is it not Abaye and Rava who both say that Rabbi Shimon, who holds that one is liable only for performing an intentional action, concedes that one is liable in a case of cut off its head, will it not die? In any case where the outcome is inevitable, as in this case where the land will be enhanced, one’s lack of intention does not exempt him. The Gemara answers: Abaye’s statement was only necessary in a case where one did so on another’s land. Since he did not intend for that outcome to eventuate and he derives no benefit from enhancing the land, he is not liable in that case.
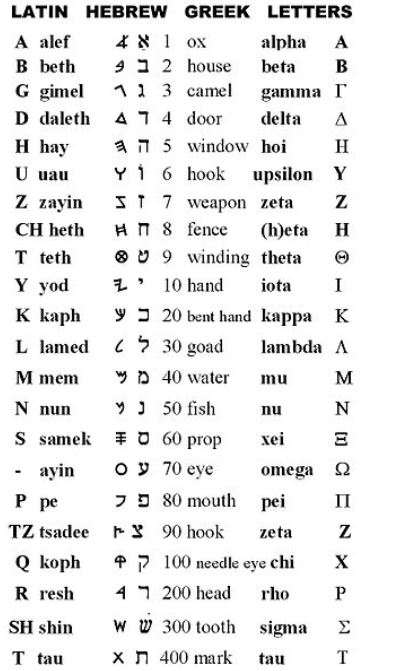
מַתְנִי׳ הַכּוֹתֵב שְׁתֵּי אוֹתִיּוֹת, בֵּין בִּימִינוֹ בֵּין בִּשְׂמֹאלוֹ, בֵּין מִשֵּׁם אֶחָד בֵּין מִשְּׁנֵי שֵׁמוֹת בֵּין מִשְׁתֵּי סַמָּנִיּוֹת, בְּכׇל לָשׁוֹן — חַיָּיב. אָמַר רַבִּי יוֹסֵי: לֹא חִיְּיבוּ שְׁתֵּי אוֹתִיּוֹת אֶלָּא מִשּׁוּם רוֹשֵׁם, שֶׁכָּךְ כּוֹתְבִין עַל קַרְשֵׁי הַמִּשְׁכָּן לֵידַע אֵיזוֹ בֶּן זוּגוֹ. אָמַר רַבִּי יְהוּדָה: מָצִינוּ שֵׁם קָטָן מִשֵּׁם גָּדוֹל — ״שֵׁם״ מִשִּׁמְעוֹן וּמִשְּׁמוּאֵל, ״נֹחַ״ מִנָּחוֹר, ״דָּן״ מִדָּנִיאֵל, ״גָּד״ מִגַּדִּיאֵל.
MISHNA: One who writes two letters on Shabbat, whether he did so with his right hand or his left, whether they were the same letter or two different letters, whether he did so using two different types of ink, in any language, he is liable. Rabbi Yosei said: One is deemed liable for writing two letters only due to marking, as they would write symbols on adjacent beams of the Tabernacle to know which beam was another beam’s counterpart. Rabbi Yehuda said: We found that one is liable for writing even if he did not complete what he was writing, so that he wrote a small name that constituted part of a longer name, e.g., Shem [shin mem] from the name Shimon or from Shmuel; Noaḥ [nun ḥet] from Naḥor; Dan [dalet nun] from Daniel; Gad [gimmel dalet] from Gaddiel. In all of these cases, the first two letters of the longer name constitute the shorter name.
גְּמָ׳ בִּשְׁלָמָא אַיָּמִין לִיחַיַּיב מִשּׁוּם דְּדֶרֶךְ כְּתִיבָה בְּכָךְ, אֶלָּא אַשְּׂמֹאל אַמַּאי? הָא אֵין דֶּרֶךְ כְּתִיבָה בְּכָךְ! אָמַר רַבִּי יִרְמְיָה: בְּאִטֵּר יָד שָׁנוּ. וְתֶהֱוֵי שְׂמֹאל דִּידֵיהּ כְּיָמִין דְּכוּלֵּי עָלְמָא, וְאַשְּׂמֹאל לִיחַיַּיב, אַיָּמִין לָא לִיחַיַּיב! אֶלָּא אָמַר אַבָּיֵי: בְּשׁוֹלֵט בִּשְׁתֵּי יָדָיו.
GEMARA: The Gemara questions the beginning of the mishna: Granted, for writing with the right hand let one be liable, as that is the typical manner of writing. However, for writing with the left hand, why is one liable? That is not the typical manner of writing. Rabbi Yirmeya said: When the mishna taught that one who writes with his left hand is liable, they taught it with regard to one who is left-handed. The Gemara asks: And if so, let his left hand have the same legal status as everyone’s right hand; for writing with his left hand, let him be liable, for writing with his right hand, let him not be liable. Rather, Abaye said: This mishna refers to an ambidextrous person, who is liable for writing with either hand.
רַב יַעֲקֹב בְּרֵהּ דְּבַת יַעֲקֹב אָמַר: הָא מַנִּי — רַבִּי יוֹסֵי הִיא, דַּאֲמַר לֹא חִיְּיבוּ שְׁתֵּי אוֹתִיּוֹת אֶלָּא מִשּׁוּם רוֹשֵׁם. וְהָא מִדְּסֵיפָא רַבִּי יוֹסֵי הִיא, רֵישָׁא לָאו רַבִּי יוֹסֵי! כּוּלָּהּ רַבִּי יוֹסֵי הִיא.
Rav Ya’akov, son of the daughter of Ya’akov, said: In accordance with whose opinion is this mishna? It is in accordance with the opinion of Rabbi Yosei, who said: One is deemed liable for writing two letters only due to marking. As such, one is liable for writing a letter even if he writes it imprecisely with his left hand. The Gemara asks: From the fact that the latter clause of the mishna is in accordance with the opinion of Rabbi Yosei, the first clause of the mishna is not in accordance with the opinion of Rabbi Yosei. The Gemara answers: That is not necessarily the case. The entire mishna is in accordance with the opinion of Rabbi Yosei, and the attribution of his second statement was for emphasis alone.
אָמַר רַבִּי יְהוּדָה, מָצִינוּ. אֶלָּא רַבִּי יְהוּדָה שְׁתֵּי אוֹתִיּוֹת וְהֵן שְׁנֵי שֵׁמוֹת הוּא דִּמְחַיֵּיב, שְׁתֵּי אוֹתִיּוֹת וְהֵן שֵׁם אֶחָד — לָא מְחַיֵּיב?
We learned in the mishna that Rabbi Yehuda said: We found that one is liable for writing even if he did not complete what he was writing, so that he wrote a small name that constituted part of a longer name. The Gemara asks: Rather, is that to say that according to Rabbi Yehuda, it is one who writes two letters that are two different types of letters who is liable; however, one who writes two letters that are one type of letter is not liable?
וְהָתַנְיָא: ״וְעָשָׂה״ — אַחַת. יָכוֹל עַד שֶׁיִּכְתּוֹב כׇּל הַשֵּׁם, וְעַד שֶׁיֶּאֱרוֹג כׇּל הַבֶּגֶד, וְעַד שֶׁיַּעֲשֶׂה כָּל הַנָּפָה — תַּלְמוּד לוֹמַר: ״מֵאַחַת״.
Wasn’t it taught in a baraita that it is written: “When a leader sinned, and he unwittingly performed one of any of the commandments which the Lord his God commanded not to do, and is guilty” (Leviticus 4:22)? The Sages taught: I might have thought that one is not guilty until he performs a complete labor, e.g., until he writes the entire name that he intended to write, or until he weaves the entire garment, or until he crafts the entire sieve made from the reeds of the warp and the woof; therefore, the verse states: “A soul who sins unintentionally in any of the Lord’s commandments which one shall not perform, and did an action from one of these” (Leviticus 4:2).
אִי ״מֵאַחַת״, יָכוֹל אֲפִילּוּ לֹא כָּתַב אֶלָּא אוֹת אַחַת, וְלֹא אָרַג אֶלָּא חוּט אֶחָד, וְלֹא עָשָׂה אֶלָּא בַּיִת אֶחָד בַּנָּפָה,
The emphasis on the phrase “from one” teaches that in order for one to be liable, it is sufficient that he perform only part of the prohibited labor. However, if that is derived from the use of the phrase “from one,” I might have thought that one is liable even if he wrote only a single letter, or even if he wove only a single thread, or even if he crafted only a single eye of the sieve, i.e., arranging the reeds to create a warp, and then interweaving a single reed as a woof;
תַּלְמוּד לוֹמַר: ״אַחַת״. הָא כֵּיצַד, אֵינוֹ חַיָּיב עַד שֶׁיִּכְתּוֹב שֵׁם קָטָן מִשֵּׁם גָּדוֹל — ״שֵׁם״ מִשִּׁמְעוֹן וּמִשְּׁמוּאֵל, ״נֹחַ״ מִנָּחוֹר, ״דָּן״ מִדָּנִיאֵל, ״גָּד״ מִגַּדִּיאֵל. רַבִּי יְהוּדָה אוֹמֵר: אֲפִילּוּ לֹא כָּתַב אֶלָּא שְׁתֵּי אוֹתִיּוֹת וְהֵן שֵׁם אֶחָד — חַיָּיב, כְּגוֹן: ״שֵׁשׁ״ ״תֵּת״, ״רָר״, ״גַּג״, ״חָח״.
therefore, the verse states “one,” which means one complete labor. How can the two phrases be reconciled? Rather it must be explained that one is liable only if he writes a small name that constitutes part of a longer name, e.g., Shem from the name Shimon or from Shmuel, Noaḥ from Naḥor, Dan from Daniel, Gad from Gaddiel. Rabbi Yehuda says: One is liable even if he wrote only two letters that are one type of letter, e.g., shesh [shin shin], tet [tav tav], rar [reish reish], gag [gimmel gimmel], ḥaḥ [ḥet ḥet].
אָמַר רַבִּי יוֹסֵי: וְכִי מִשּׁוּם כּוֹתֵב הוּא חַיָּיב?! וַהֲלֹא אֵינוֹ חַיָּיב אֶלָּא מִשּׁוּם רוֹשֵׁם, שֶׁכֵּן רוֹשְׁמִין עַל קַרְשֵׁי הַמִּשְׁכָּן לֵידַע אֵיזוֹ הִיא בֶּן זוּגוֹ. לְפִיכָךְ, שָׂרַט שְׂרִיטָה אַחַת עַל שְׁנֵי נְסָרִין, אוֹ שְׁתֵּי שְׂרִיטוֹת עַל נֶסֶר אֶחָד — חַיָּיב.
Rabbi Yosei said: And is one liable due to the labor of writing? Isn’t one liable only due to the prohibition of marking, as they would write symbols on adjacent beams of the Tabernacle to know which beam was another beam’s counterpart? Therefore, one who made a single scratch on two boards, or two scratches on a single board, is liable.
רַבִּי שִׁמְעוֹן אוֹמֵר: ״וְעָשָׂה אַחַת״, יָכוֹל עַד שֶׁיִּכְתּוֹב אֶת כָּל הַשֵּׁם, עַד שֶׁיֶּאֱרוֹג כׇּל הַבֶּגֶד, עַד שֶׁיַּעֲשֶׂה אֶת כָּל הַנָּפָה — תַּלְמוּד לוֹמַר: ״מֵאַחַת״. אִי ״מֵאַחַת״, יָכוֹל אֲפִילּוּ לֹא כָּתַב אֶלָּא אוֹת אַחַת, וַאֲפִילּוּ לֹא אָרַג אֶלָּא חוּט אֶחָד, וַאֲפִילּוּ לֹא עָשָׂה אֶלָּא בַּיִת אֶחָד בַּנָּפָה — תַּלְמוּד לוֹמַר: ״אַחַת״. הָא כֵּיצַד? אֵינוֹ חַיָּיב עַד שֶׁיַּעֲשֶׂה מְלָאכָה שֶׁכַּיּוֹצֵא בָּהּ מִתְקַיֶּימֶת.
Rabbi Shimon says: The verse states, “When a leader sinned, and he unwittingly performed one of any of the commandments which the Lord his God commanded not to do, and is guilty” (Leviticus 4:22), and from the word one, I might have thought that one is not guilty until he performs a complete labor, e.g., until he writes the entire name that he intended to write, or until he weaves the entire garment, or until he crafts the entire sieve made from the reeds of the warp and the woof; therefore, the verse states “from one.” However, if that is derived from the use of the phrase “from one,” I might have thought that one is liable even if he wrote only a single letter, or even if he wove only a single thread, or even if he crafted only a single eye of the sieve. Therefore, the verse states “one.” But how can we reconcile the two phrases? One is only liable for performing a labor that is of the type that endures. In that case it is considered a complete labor.
רַבִּי יוֹסֵי אוֹמֵר: ״וְעָשָׂה אַחַת״ ״וְעָשָׂה הֵנָּה״, פְּעָמִים שֶׁחַיָּיב אַחַת עַל כּוּלָּן, וּפְעָמִים שֶׁחַיָּיב עַל כׇּל אַחַת וְאַחַת.
Rabbi Yosei says that the verse states: “And did an action from one of these” (Leviticus 4:2). This unusual expression indicates repetition: And he performed one, and he performed these. From here it is derived that at times one is liable to bring one sin-offering for them all, and at times one is liable to bring several offerings, one for each and every one.
קָתָנֵי מִיהָא: רַבִּי יְהוּדָה אוֹמֵר אֲפִילּוּ לֹא כָּתַב אֶלָּא שְׁתֵּי אוֹתִיּוֹת וְהֵן שֵׁם אֶחָד — חַיָּיב. לָא קַשְׁיָא: הָא דִּידֵיהּ, הָא דְרַבֵּיהּ. דְּתַנְיָא, רַבִּי יְהוּדָה אוֹמֵר מִשּׁוּם רַבָּן גַּמְלִיאֵל: אֲפִילּוּ לֹא כָּתַב אֶלָּא שְׁתֵּי אוֹתִיּוֹת וְהֵן שֵׁם אֶחָד — חַיָּיב, כְּגוֹן ״שֵׁשׁ״, ״תֵּת״, ״רָר״, ״גַּג״, ״חָח״.
The Gemara returns to the matter of the baraita: In any event, it was taught that Rabbi Yehuda says: One is liable even if he only wrote two letters that are one type of letter; he does not insist that one is liable only if he writes two different letters. The Gemara answers: This is not difficult. This opinion is his own, and that other opinion is that of his teacher, as it was taught in a baraita: Rabbi Yehuda says in the name of Rabban Gamliel: Even if one only wrote two identical letters, forming words such as shesh, tet, rar, gag, or ḥaḥ, he is liable. That is Rabban Gamliel’s opinion, but Rabbi Yehuda himself holds that one is only liable for writing two different letters.
רַבִּי שִׁמְעוֹן הַיְינוּ תַּנָּא קַמָּא? וְכִי תֵּימָא אָלֶ״ף אָלֶ״ף דַּ״אֲאַזֶּרְךָ״ אִיכָּא בֵּינַיְיהוּ, דְּתַנָּא קַמָּא סָבַר אָלֶ״ף אָלֶ״ף דַּ״אֲאַזֶּרְךָ״ לָא מִיחַיַּיב, וְרַבִּי שִׁמְעוֹן סָבַר כֵּיוָן דְּאִיתֵיהּ בִּגְלָטוֹרֵי בְּעָלְמָא — חַיָּיב, לְמֵימְרָא דְּרַבִּי שִׁמְעוֹן לְחוּמְרָא?
The Gemara asks: The opinion of Rabbi Shimon in the baraita is identical to the opinion of the first tanna. And if you say that there is a practical difference between their opinions in the case of the letters alef alef in a word such as a’azerkha (Isaiah 45:5), in that the first tanna holds that if one wrote the letters alef alef of the word a’azerkha he is not liable because the two letters do not spell a complete word, and Rabbi Shimon holds that since that combination of letters appears in standard amulets [gelatorei] he is liable because this writing is considered to be enduring; is that to say that the opinion of Rabbi Shimon tends to stringency in this matter?
וְהָתַנְיָא: הַקּוֹדֵחַ כׇּל שֶׁהוּא חַיָּיב, הַמְגָרֵר כׇּל שֶׁהוּא, הַמְעַבֵּד כׇּל שֶׁהוּא, הַצָּר בִּכְלִי צוּרָה כׇּל שֶׁהוּא. רַבִּי שִׁמְעוֹן אוֹמֵר: עַד שֶׁיִּקְדַּח אֶת כּוּלּוֹ, עַד שֶׁיִּגְרוֹר אֶת כּוּלּוֹ, עַד שֶׁיְּעַבֵּד אֶת כּוּלּוֹ, עַד שֶׁיָּצוּר כּוּלּוֹ.
Wasn’t it taught in a baraita: One who drills a hole of any size on Shabbat is liable, one who scrapes and smooths posts or parchments in any amount is liable, one who tans any amount of an animal hide is liable, one who draws any size form on a vessel is liable? Rabbi Shimon says: One is liable only if he drills the entire hole that he intended to drill, or if he scrapes the entire post or parchment that he intended to scrape, or if he tans the entire hide that he intended to tan, or if he draws the entire form that he intended to draw. Clearly, Rabbi Shimon’s opinion is the lenient one.
אֶלָּא, רַבִּי שִׁמְעוֹן הָא אֲתָא לְאַשְׁמוֹעִינַן, עַד שֶׁיִּכְתּוֹב אֶת הַשֵּׁם כּוּלּוֹ. וּמִי מָצֵית אָמְרַתְּ הָכִי? וְהָתַנְיָא, רַבִּי שִׁמְעוֹן אוֹמֵר: ״וְעָשָׂה אַחַת״, יָכוֹל עַד שֶׁיִּכְתּוֹב אֶת הַשֵּׁם כּוּלּוֹ — תַּלְמוּד לוֹמַר: ״מֵאַחַת״! תָּרֵיץ וְאֵימָא הָכִי: יָכוֹל עַד שֶׁיִּכְתּוֹב אֶת הַפָּסוּק כּוּלּוֹ — תַּלְמוּד לוֹמַר: ״מֵאַחַת״.
Rather, Rabbi Shimon comes to teach us this: It is considered writing that endures only if he writes the entire name. The Gemara asks: And how can you say this? Wasn’t it taught in a baraita that Rabbi Shimon says: From the phrase “and he performed one” I might have thought that one is liable only if he writes the entire name; therefore, the verse states “from one.” Apparently, he does not require that the entire word be written in order to be liable. The Gemara answers: Resolve the contradiction between these statements and say this: I might have thought that one is liable only if he writes the entire verse that he intended to write; therefore, the verse states “from one.” One is liable for writing less than that. However, one is certainly not liable for writing less than a complete word.
רַבִּי יוֹסֵי אוֹמֵר: ״וְעָשָׂה אַחַת״ ״וְעָשָׂה הֵנָּה״ — פְּעָמִים שֶׁחַיָּיב אַחַת עַל כּוּלָּן, וּפְעָמִים שֶׁחַיָּיב עַל כׇּל אַחַת וְאַחַת.
The baraita cites that Rabbi Yosei says that the verse states: “And did an action from one of these.” This unusual expression indicates repetition and it is as if it says: And he did one, and he did these. From here it is derived that at times one is liable to bring one sin-offering for them all, and at times one is liable to bring several offerings, one for each and every one.
אָמַר רַבִּי יוֹסֵי בְּרַבִּי חֲנִינָא: מַאי טַעְמָא דְּרַבִּי יוֹסֵי ״אַחַת״ ״מֵאַחַת״, ״הֵנָּה״ ״מֵהֵנָּה״, אַחַת שֶׁהִיא ״הֵנָּה״, וְ״הֵנָּה״ שֶׁהִיא אַחַת.
And Rabbi Yosei, son of Rabbi Ḥanina, said: What is the reason for Rabbi Yosei’s opinion? Since the verse says “from one” and “of these,” Rabbi Yosei detects both a restriction, i.e., “from” and “of,” an amplification based on superfluous expressions, as it would have been sufficient for the verse to say “one” and not “from one,” and it would have been sufficient to say “these” instead of “of these.” The repetitive language teaches that there are cases of one that is these and cases of these that are one.
״אַחַת״ — ״שִׁמְעוֹן״, ״מֵאַחַת״ — ״שֵׁם״ מִ״שִּׁמְעוֹן״. ״הֵנָּה״ — אָבוֹת, ״מֵהֵנָּה״ — תּוֹלָדוֹת. אַחַת שֶׁהִיא הֵנָּה — זְדוֹן שַׁבָּת וְשִׁגְגַת מְלָאכוֹת. הֵנָּה שֶׁהִיא אַחַת — שִׁגְגַת שַׁבָּת וּזְדוֹן מְלָאכוֹת.
Similarly, Rabbi Yosei explained that had the verse said “one,” the conclusion would have been that one is only liable for performing a complete transgression, e.g., writing the name Shimon on Shabbat. “From one” teaches that one is liable even if he does not complete the intended action, e.g., writing Shem from Shimon. “These” refers to the transgressions themselves, e.g., the primary categories of labor prohibited on Shabbat. The words “from these” teach that even subcategories are included. The Gemara illustrates the case of one that is these. One was aware that he was in violation of the prohibition of Shabbat but not aware that the individual labors were prohibited. In that case, if he performed several prohibited labors during this lapse of awareness, he is liable to bring a sin-offering for each violation. These that are one refers to a case where one was unaware that he was in violation of the prohibition of Shabbat but he was aware that the individual labors were prohibited. In that case, he is liable to bring only one sin-offering for all of the prohibited labors.
אָמַר רַבִּי יְהוּדָה: מָצִינוּ שֵׁם קָטָן מִשֵּׁם גָּדוֹל. מִי דָּמֵי? מֵ״ם דְּ״שֵׁם״ סָתוּם, מֵ״ם דְּ״שִׁמְעוֹן״ פָּתוּחַ! אָמַר רַב חִסְדָּא: זֹאת אוֹמֶרֶת סָתוּם וַעֲשָׂאוֹ פָּתוּחַ — כָּשֵׁר.
We learned in the mishna that Rabbi Yehuda said: We found that one is liable for writing even if he did not complete what he was writing and wrote a small name that constituted part of a longer name, e.g., Shem from Shimon. The Gemara asks: Is it similar? The mem in Shem is closed and the mem in Shimon is open. Rav Ḥisda said: That is to say that a closed letter that one rendered open is valid even in writing a Torah scroll, and it is not considered an irregularity in the writing. Therefore, one is liable for writing an open letter instead of a closed one.
מֵיתִיבִי: ״וּכְתַבְתָּם״ — שֶׁתְּהֵא כְּתִיבָה תַּמָּה, שֶׁלֹּא יִכְתּוֹב אַלְפִין עַיְינִין, עַיְינִין אַלְפִין. בֵּיתִין כָּפִין, כָּפִין בֵּיתִין. גַּמִּין צָדִין, צָדִין גַּמִּין. דַּלְתִין רֵישִׁין, רֵישִׁין דַּלְתִין. הֵיהִין חֵיתִין, חֵיתִין הֵיהִין. וָוִין יוֹדִין, יוֹדִין וָוִין. זַיְינִין נוּנִין, נוּנִין זַיְינִין. טֵיתִין פֵּיפִין, פֵּיפִין טֵיתִין.
The Gemara raised an objection from a baraita that interprets the verse: “And you shall write them on the doorposts of your house and on your gates” (Deuteronomy 6:9). “And you shall write them [ukhtavtam]” means that it should be perfect writing [ketiva tamma] with no mistakes, and clear writing. This means that one should not write an alef as an ayin, an ayin as an alef, a beit as a kaf, a kaf as a beit, a gimmel as a tzadi, a tzadi as a gimmel, a dalet as a reish, a reish as a dalet, a heh as a ḥet, a ḥet as a heh, a vav as a yod, a yod as a vav, a zayin as a nun, a nun as a zayin, a tet as a peh, a peh as a tet.
כְּפוּפִין פְּשׁוּטִין, פְּשׁוּטִין כְּפוּפִין. מֵימִין סָמְכִין, סָמְכִין מֵימִין. סְתוּמִין פְּתוּחִין, פְּתוּחִין סְתוּמִין. פָּרָשָׁה פְּתוּחָה לֹא יַעֲשֶׂנָּה סְתוּמָה, סְתוּמָה לֹא יַעֲשֶׂנָּה פְּתוּחָה. כְּתָבָהּ כְּשִׁירָה, אוֹ שֶׁכָּתַב אֶת הַשִּׁירָה כַּיּוֹצֵא בָהּ, אוֹ שֶׁכָּתַב שֶׁלֹּא בִּדְיוֹ, אוֹ שֶׁכָּתַב אֶת הָאַזְכָּרוֹת בְּזָהָב — הֲרֵי אֵלּוּ יִגָּנְזוּ.
Similarly, one should not write bent letters like kaf and nun found in the middle of a word as straight letters like kaf and nun found at the end of a word, nor should one write straight letters as bent letters. A final mem should not be written like a samekh, and a samekh should not be written like a mem. A closed mem should not be written open, and an open one should not be written closed. Similarly, if there is an open paragraph in the Torah one may not render it closed, and one may not render a closed paragraph open. If one wrote a mezuza or a Torah scroll following the Torah’s format for poetry or if one wrote poetry like regular text, as a mezuza is typically written, or if one wrote without ink but with another material, or if one wrote the mentions of God’s names in gold, all of these must be suppressed. Apparently, one may not write closed letters as open letters, contrary to the statement of Rav Ḥisda.
הוּא דְּאָמַר כִּי הַאי תַּנָּא, דְּתַנְיָא, רַבִּי יְהוּדָה בֶּן בְּתִירָה אוֹמֵר: נֶאֱמַר בַּשֵּׁנִי ״וְנִסְכֵּיהֶם״. בַּשִּׁשִּׁי ״וּנְסָכֶיהָ״, בַּשְּׁבִיעִי ״כְּמִשְׁפָּטָם״, הֲרֵי מֵ״ם יוֹ״ד מֵ״ם — ״מַיִם״, מִכָּאן רֶמֶז לְנִיסּוּךְ מַיִם מִן הַתּוֹרָה.
The Gemara answers: Rav Ḥisda stated his opinion in accordance with the opinion of this tanna, as it was taught in a baraita that Rabbi Yehuda ben Beteira says: While on the rest of the days of Sukkot the verse employs the phrase: “And its libation [veniska],” on the second day it is stated: “And their libations [veniskeihem]” (Numbers 29:19) with an extra letter mem; on the sixth day, it is stated: “And its libations [unsakhe’ah]” (Numbers 29:31) with an extra letter yod. On the seventh day, instead of “according to the law [kamishpat]” employed on the other days, it is stated: “According to their laws [kemishpatam]” (Numbers 29:33) with an extra letter mem. Together these additional letters, mem, yod, and mem, form the word mayim, which means water. This is an allusion to the water libation from the Torah. On Sukkot, a water libation was poured onto the altar in addition to the wine libation that accompanied sacrifices throughout the year. However, here, the closed mem at the end of the word veniskeihem is interpreted as if it were an open mem and used as the first mem in mayim.
וּמִדְּפָתוּחַ וַעֲשָׂאוֹ סָתוּם — כָּשֵׁר, סָתוּם נָמֵי סָתוּם וַעֲשָׂאוֹ פָּתוּחַ — כָּשֵׁר.
And from the fact that an open letter that one rendered closed is valid, in the case of a closed letter, too, a closed letter that one rendered open is valid. This homiletic interpretation supports Rav Ḥisda’s opinion.
מִי דָּמֵי? פָּתוּחַ וַעֲשָׂאוֹ סָתוּם —
The Gemara rejects this comparison: Is it similar? If one rendered an open letter closed,