Beitzah 38
וְהָוֵינַן בַּהּ: מַאי שְׁנָא לְכָאן וּלְכָאן דְּלָא — דְּאֵין בְּרֵירָה, מִזְרָח וּמַעֲרָב נָמֵי אֵין בְּרֵירָה!
And we discussed the following difficulty with regard to this teaching of Ayo: What is different about the case where two rabbis are coming to the two locations, one here and the other there, and one places two eiruvin, planning to decide on Shabbat which lecture he will attend? Why did Rabbi Yehuda state that this may not be done? It is because he held that there is no retroactive designation. But if so, in the first case as well, where only one rabbi comes, but the location of his lecture was not known before Shabbat, and one placed eiruvin in the east and the west, we should say that neither is effective because the rabbi’s location will not be known until Shabbat, and there is no retroactive designation.
וְאָמַר רַבִּי יוֹחָנָן: וּכְבָר בָּא חָכָם. אַלְמָא: לֵית לֵיהּ לְרַבִּי יוֹחָנָן בְּרֵירָה!
And Rabbi Yoḥanan said in explanation: This first case is referring to a situation in which the rabbi had already arrived before the eiruv was placed, but the one placing the eiruv does not know the rabbi’s location. Therefore, it had already been determined which of the two eiruvin would be effective, although it was not yet known to him when Shabbat began. Apparently, then, Rabbi Yoḥanan does not accept the principle of retroactive designation even in matters of rabbinic law, as he states that if the rabbi were to arrive after the eiruv was placed, it would not be effective retroactively.
אֶלָּא: לְעוֹלָם לָא תֵּיפוֹךְ, וְכִי לֵית לֵיהּ לְרַבִּי אוֹשַׁעְיָא בְּרֵירָה — בִּדְאוֹרָיְיתָא, אֲבָל בִּדְרַבָּנַן — אִית לֵיהּ.
Rather, the Gemara rejects this approach and states: Actually, do not reverse the views of Rabbi Yoḥanan and Rabbi Hoshaya; it is indeed Rabbi Hoshaya, also known as Rabbi Oshaya, who accepts retroactive designation, and Rabbi Yoḥanan who rejects it. As for Rabbi Oshaya’s statement with regard to the entrances to a house that contains a corpse, the following answer may be offered: And when does Rabbi Oshaya not hold of the principle of retroactive designation? With regard to matters of Torah law, such as the ritual impurity of the dead. But with regard to matters of rabbinic law, such as Shabbat limits and the placement of eiruvin, he does accept this principle.
דָּרֵשׁ מָר זוּטְרָא: הֲלָכָה כְּרַבִּי אוֹשַׁעְיָא.
Mar Zutra taught in a public lesson: The halakha is in accordance with the opinion of Rabbi Oshaya with regard to retroactive designation.
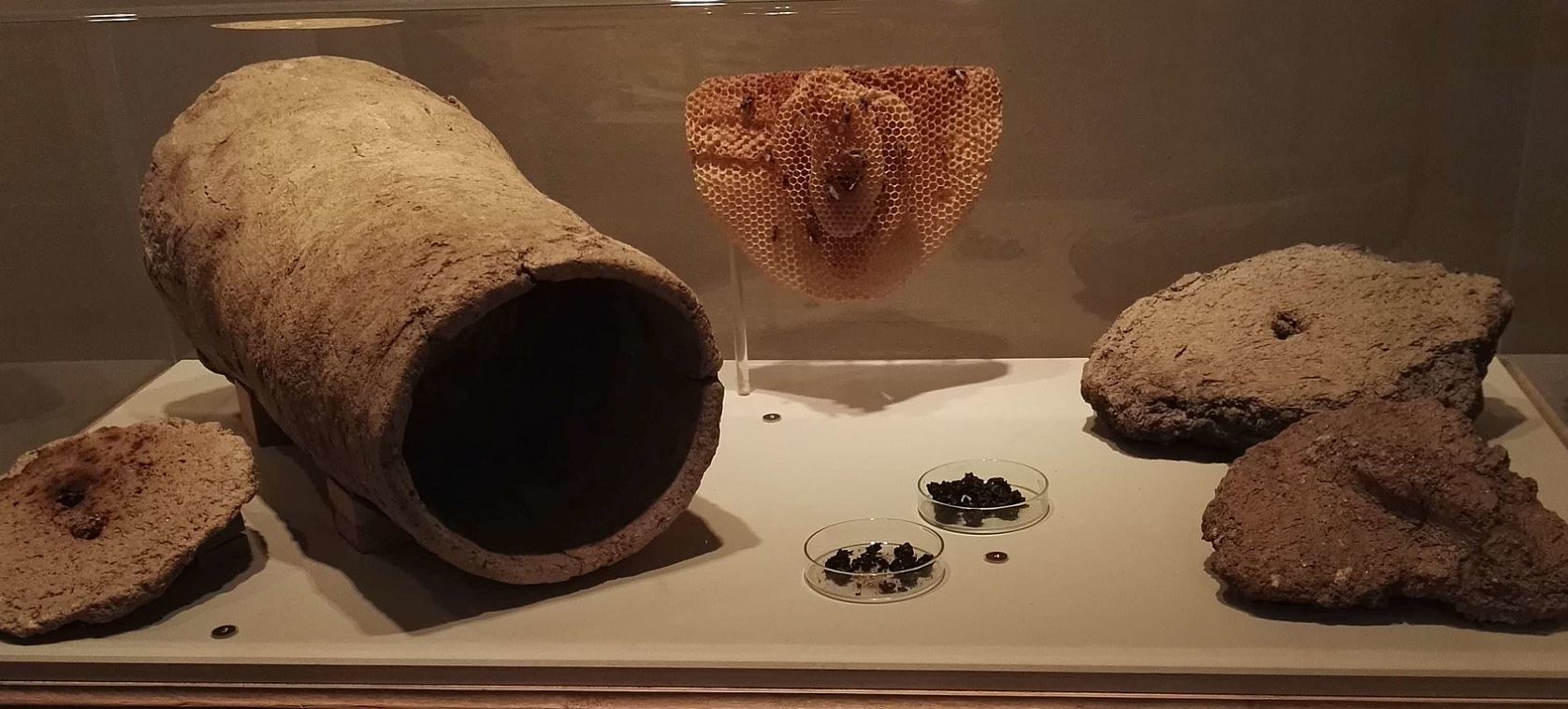
אָמַר שְׁמוּאֵל: שׁוֹר שֶׁל פַּטָּם — הֲרֵי הוּא כְּרַגְלֵי כׇּל אָדָם. שׁוֹר שֶׁל רוֹעֶה — הֲרֵי הוּא כְּרַגְלֵי אוֹתָהּ הָעִיר.
Shmuel said: An ox of a fattener, one whose occupation is to fatten oxen in order to sell them for their meat, is as the feet of all people. It is as the feet of the one who acquires the animal on the Festival, even if the buyer is from another city, as the fattener’s intention when the Festival begins is that the ox belong to whoever buys it. But an ox of a shepherd, who raises oxen for himself but occasionally sells them to his neighbors or acquaintances, is as the feet of the people of that city, as his intention when the Festival begins is that he might sell the animal to someone in town, but not to someone from out of town.
הַשּׁוֹאֵל כְּלִי מֵחֲבֵירוֹ מֵעֶרֶב יוֹם טוֹב. פְּשִׁיטָא! לָא צְרִיכָא, שֶׁלֹּא מְסָרוֹ לוֹ אֶלָּא בְּיוֹם טוֹב. מַהוּ דְּתֵימָא: לָאו בִּרְשׁוּתֵיהּ אוֹקְמֵיהּ, קָא מַשְׁמַע לַן.
§ The mishna states: In the case of one who borrows a vessel from another on the eve of a Festival, it is as the feet of the borrower. The Gemara asks: It is obvious that this is the case, as the place of rest of the vessel has already been established in the possession of the borrower. The Gemara answers: No, it is necessary to state this halakha in a case where one did not deliver the vessel to him until the Festival itself. Lest you say: Since the lender did not establish it in the borrower’s possession before the Festival began, it should remain as the feet of the lender, the mishna therefore teaches us that it is not so, but it is as the feet of the borrower.
מְסַיַּיע לֵיהּ לְרַבִּי יוֹחָנָן, דְּאָמַר רַבִּי יוֹחָנָן: הַשּׁוֹאֵל כְּלִי מֵחֲבֵירוֹ מֵעֶרֶב יוֹם טוֹב, אַף עַל פִּי שֶׁלֹּא נְתָנוֹ לוֹ אֶלָּא בְּיוֹם טוֹב — הֲרֵי הוּא כְּרַגְלֵי הַשּׁוֹאֵל.
The Gemara comments: Interpreted in this manner, the mishna supports a statement of Rabbi Yoḥanan, as Rabbi Yoḥanan said: One who borrows a vessel from another on the eve of a Festival, even if he did not give it to him until the Festival itself, it is as the feet of the borrower.
בְּיוֹם טוֹב — כְּרַגְלֵי הַמַּשְׁאִיל. פְּשִׁיטָא! לָא צְרִיכָא, דִּרְגִיל וְשָׁאֵיל מִינֵּיהּ, מַהוּ דְּתֵימָא: בִּרְשׁוּתֵיהּ קָא מוֹקֵים לֵיהּ, קָא מַשְׁמַע לַן, מֵימָר אָמַר: דִּלְמָא מַשְׁכַּח אִינִישׁ אַחֲרִינָא וְאָזֵיל וְשָׁאֵיל מִינֵּיהּ.
§ It is taught in the mishna: If one borrowed on the Festival itself, it is as the feet of the lender. The Gemara again wonders: This is obvious. The Gemara answers: No, it is necessary to state this halakha in a case where this borrower is accustomed to borrowing such items from this lender. Lest you say that since it is a regular occurrence for this loan to take place, the lender establishes it in his possession ahead of time, and it should therefore be considered as though the object’s place of rest is established as the feet of the borrower, the mishna therefore teaches us that it is not so, as the lender certainly says to himself: Perhaps he will find someone else this time, and he will go and borrow from him. Consequently, the lender does not transfer possession of the object to the borrower until the latter takes it, and it may be carried only where the lender may go.
וְכֵן הָאִשָּׁה שֶׁשָּׁאֲלָה מֵחֲבֶרְתָּהּ. כִּי סְלֵיק רַבִּי אַבָּא אָמַר: יְהֵא רַעֲוָא דְּאֵימָא מִלְּתָא דְּתִתְקַבַּל. כִּי סְלֵיק, אַשְׁכְּחֵיהּ לְרַבִּי יוֹחָנָן וְרַבִּי חֲנִינָא בַּר פַּפִּי וְרַבִּי זֵירָא, וְאָמְרִי לַהּ רַבִּי אֲבָהוּ וְרַבִּי שִׁמְעוֹן בֶּן פַּזִּי וְרַבִּי יִצְחָק נַפָּחָא, וְיָתְבִי וְקָאָמְרִי: אַמַּאי? וְלִבְטִיל מַיִם וָמֶלַח לְגַבֵּי עִיסָּה! אֲמַר לְהוּ רַבִּי אַבָּא:
§ It is taught in the mishna: And similarly, a woman who borrowed spices from another to put in a dish, or water and salt to put in her dough, these are as the feet of both of them. The Gemara relates: When Rabbi Abba ascended from Babylonia to Eretz Yisrael, he said: May it be God’s will that I say a statement of halakha that will be accepted by my listeners in Eretz Yisrael, so that I will not be put to shame. When he ascended, he found Rabbi Yoḥanan, Rabbi Ḥanina bar Pappi, and Rabbi Zeira, and some say he found Rabbi Abbahu, Rabbi Shimon ben Pazi, and Rabbi Yitzḥak Nappaḥa, and they were sitting and saying in a discussion of the mishna: Why is this the halakha with regard to dough? But let the water and salt be considered nullified in the dough, and the status of the dough should follow its flour rather than its minor ingredients, such as water and salt. Rabbi Abba said to them:
הֲרֵי שֶׁנִּתְעָרֵב לוֹ קַב חִטִּין בַּעֲשָׂרָה קַבִּין חִטִּין שֶׁל חֲבֵירוֹ, יֹאכַל הַלָּה וְחָדֵי?! אַחִיכוּ עֲלֵיהּ. אֲמַר לְהוּ: גּוּלְּתַיְכוּ שְׁקַלִי? הֲדוּר אַחִיכוּ עֲלֵיהּ.
If one’s single kav of wheat became mingled with ten kav of another’s wheat, shall the latter eat all eleven kav and rejoice? One does not allow his property to become nullified into someone else’s property. The same applies to water and salt in dough. The Sages laughed at him. He said to them: Did I take your cloaks from you that you are putting me to shame? They again laughed at him.
אָמַר רַב אוֹשַׁעְיָא: שַׁפִּיר עֲבוּד דְּאַחִיכוּ עֲלֵיהּ. מַאי שְׁנָא חִטִּין בִּשְׂעוֹרִים דְּלָא קָאָמַר לְהוּ — דְּהָוֵה לֵיהּ מִין בְּשֶׁאֵינוֹ מִינוֹ, וּמִין בְּשֶׁאֵינוֹ מִינוֹ — בָּטֵיל. חִטִּין בְּחִטִּין נָמֵי, נְהִי דִּלְרַבִּי יְהוּדָה לֹא בָּטֵיל, לְרַבָּנַן מִבְטָל בָּטֵיל.
Rabbi Oshaya said: They did well to laugh at him. They were correct that the two cases are dissimilar, as they reasoned as follows: What is different about a case of wheat belonging to one person that became mingled with barley of another, that Rabbi Abba did not say this case to them as an example? He specifically chose an example of wheat mingling with other wheat and not that case of barley because that is one type mingled with something that is not its same type. The principle is: A type of food mixed with a large amount of food not of its own type becomes nullified, and this principle applies even when the two foods belong to two different people. If so, the same may be said when wheat of one individual is mixed with wheat of another as well. Although, according to Rabbi Yehuda, an item mingled with another item of the same type is not nullified, according to the Rabbis it is certainly nullified.
אֲמַר לֵיהּ רַב סָפְרָא: מֹשֶׁה! שַׁפִּיר קָאָמְרַתְּ?! וְלָא שְׁמִיעַ לְהוּ הָא דְּאָמַר רַבִּי חִיָּיא קְטוֹסְפָאָה מִשְּׁמֵיהּ דְּרַב: הַבּוֹרֵר צְרוֹרוֹת מִגׇּרְנוֹ שֶׁל חֲבֵרוֹ — חַיָּיב לְשַׁלֵּם לוֹ דְּמֵי חִטִּים.
Rav Safra said to Rabbi Oshaya: Moses! This is a term of reverence for the leader of the generation. Have you in fact spoken well in defending those who scoffed at Rabbi Abba? But, did those Sages who scoffed not hear of this teaching that Rabbi Ḥiyya of Ketosfa’a said in the name of Rav: One who removes pebbles from another’s wheat granary is obligated to reimburse him for the loss he has caused and pay him the value of wheat according to the weight of those stones. The latter could have sold those pebbles along with his wheat, as there is always some refuse mixed in with the wheat that is weighed and sold along with it. Therefore, the removal of the pebbles has caused the owner of the granary a monetary loss.
אַלְמָא: כַּיְלָא חַסְּרֵיהּ. הָכָא נָמֵי — כַּיְלָא חַסְּרֵיהּ.
Apparently, he must compensate him because he has reduced his measure of wheat. Despite the fact that the pebbles themselves are worthless, we do not say that the pebbles were nullified in the wheat and that consequently there is no loss involved in their removal. Here, too, in the case of one who borrows water and salt, which are not worthless, all the more so may we say that one has reduced his measure, and he must compensate the lender; it cannot be said that they are nullified in the dough and that they are no longer taken into account regarding the Shabbat limit.
אֲמַר לֵיהּ אַבָּיֵי: וְלָא שָׁנֵי לֵיהּ לְמָר בֵּין מָמוֹן שֶׁיֵּשׁ לוֹ תּוֹבְעִין לְמָמוֹן שֶׁאֵין לוֹ תּוֹבְעִין?
Abaye objected to the comparison to the case with the pebbles in the wheat, and said to Rav Safra: And does the master not differentiate between money that has claimants, such as in the case of the pebbles removed from the granary in which the owner seeks compensation and therefore there is no nullification, and money that does not have claimants, as in the case of water and salt, where the owner lent them to the borrower and does not demand them back for now? In the latter case it is possible for these ingredients to be considered nullified.
אֲמַר לֵיהּ: וְלִיטַעְמָיךְ, הָא דְּאָמַר רַב חִסְדָּא: נְבֵלָה בְּטֵלָה בִּשְׁחוּטָה, לְפִי שֶׁאִי אֶפְשָׁר לַשְּׁחוּטָה שֶׁתֵּעָשֶׂה נְבֵלָה.
Rav Safra said to him: And according to your reasoning, that one must distinguish between money that has claimants and money that does not, how would you account for this teaching: Rav Ḥisda said: According to Rabbi Yehuda, who maintains that an item can be nullified only when mixed with an item of a different type but not of the same type, flesh of an unslaughtered animal carcass can be nullified in a larger quantity of meat of a slaughtered animal. Although carcass meat generally imparts impurity, if someone touches the mixture of the two meats he does not become ritually impure, as the carcass meat is considered a different type from the slaughtered animal, and is therefore nullified. This is because meat from a slaughtered animal cannot attain the status of carcass, and it is therefore viewed as a different type.
שְׁחוּטָה אֵינָהּ בְּטֵלָה בִּנְבֵלָה, לְפִי שֶׁאֶפְשָׁר לַנְּבֵלָה שֶׁתֵּעָשֶׂה שְׁחוּטָה.
The Gemara continues to cite Rav Ḥisda’s statement: However, if meat of a slaughtered animal became mingled with a larger quantity of pieces of animal carcass, the meat of the slaughtered animal is not nullified by the carcass, as it is possible for a carcass to attain the status of a slaughtered animal. This means that it can lose its ability to transmit ritual impurity, as if a carcass becomes spoiled to the extent that it is no longer edible, it loses its impure status. The fact that the carcass meat has the potential ability to attain the status of slaughtered meat renders the two meats as the same type, and according to Rabbi Yehuda the smaller amount of slaughtered meat would not be nullified in the larger amount of carcass meat. The entirety of the mixture would not be considered carcass meat, but would retain its status of intermingled carcass and slaughtered meat.
הָכִי נָמֵי דְּכִי אִית לַהּ בְּעָלִים — לָא בָּטְלָה? וְכִי תֵּימָא הָכִי נָמֵי — וְהָא תַּנְיָא, אָמַר רַבִּי יוֹחָנָן בֶּן נוּרִי: חֶפְצֵי הֶפְקֵר קוֹנִין שְׁבִיתָה. אַף עַל פִּי שֶׁאֵין לָהֶם בְּעָלִים — דּוֹמִין כְּמִי שֶׁיֵּשׁ לָהֶם בְּעָלִים.
Here, too, will you say that if the carcass has owners other than the owner of the slaughtered meat, it is not nullified in the slaughtered meat? And if you say: Yes, it is indeed so, but isn’t it taught: Rabbi Yoḥanan ben Nuri said: Ownerless objects acquire residence for Shabbat in their location, and anyone who finds them on Shabbat may move them two thousand cubits in all directions but not beyond that, as although they have no owner, it is as though they have an owner? This shows that even property that has no claimants, like the salt and water in this mishna, has its own independent Shabbat limits, which do not become nullified when mixed with items that have a different Shabbat limit.
אֲמַר לֵיהּ: מִי קָא מְדַמֵּית אִיסּוּרָא לְמָמוֹנָא? אִיסּוּרָא — בָּטֵיל, מָמוֹנָא — לֹא בָּטֵיל.
Abaye said to Rav Safra: Are you comparing a halakha involving prohibitions, i.e., ritual law, to monetary law? An object subject to a prohibition, such as a prohibited food, can be nullified, whereas one’s money cannot be nullified.
וְטַעְמָא מַאי?
Therefore, the initial question remains: Why isn’t the small amount of salt and water in the dough, which is subject to the ritual restriction of Shabbat limits, nullified in the rest of the dough, in the manner of nullification of all other ritual prohibitions? And what is the reason that the water and salt are not nullified in the dough?
אַבָּיֵי אָמַר: גְּזֵרָה שֶׁמָּא תַּעֲשֶׂה עִיסָּה בְּשׁוּתָּפוּת.
Abaye said: It is a decree that the Sages made, lest a woman make dough in partnership with her neighbors. Indeed, in the case of the mishna, the small amount she received from her neighbor should be nullified in the dough. However, on another occasion, several friends or neighbors might decide to pool ingredients and prepare bread in partnership, in which case the bread is certainly bound by the Shabbat limits of all the parties combined. In order to prevent confusion between making dough in partnership and making it with borrowed ingredients, the Sages made a decree that the dough in both cases be subject to the same limitations.
רָבָא אָמַר: תַּבְלִין לְטַעְמָא עֲבִידִי, וְטַעְמָא לָא בָּטֵיל.
Rava said a different reason: Spices are made in order to add taste to food, and taste is not nullified, even if the amount of actual substance is minute. Nullification indicates that a small amount of food may be considered insignificant and therefore null and void, but if an ingredient is added with the specific intent that its taste be noticed, there can be no nullification.